Intro
Learn about Tubes Tied Surgery, a permanent birth control method, in our comprehensive guide, covering tubal ligation, procedure, recovery, and risks, to help women make informed decisions about female sterilization and family planning options.
Tubal ligation, commonly referred to as "getting one's tubes tied," is a surgical procedure for female sterilization and/or permanent birth control. The process involves cutting, blocking, or sealing the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. This method is highly effective, with a failure rate of less than 1%. Despite its effectiveness, it's crucial for individuals considering this procedure to understand its implications, benefits, and potential risks.
The decision to undergo tubal ligation is deeply personal and often influenced by various factors, including family size, health considerations, and personal beliefs. It's a permanent form of birth control, meaning that once the procedure is done, it is very difficult to reverse. Therefore, it's essential for individuals to be certain about their decision and to discuss it thoroughly with their healthcare provider.
Understanding the procedure, its benefits, and its potential drawbacks is key to making an informed decision. Tubal ligation can be performed in several ways, including laparoscopic surgery, where small incisions are made in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) and surgical instruments. Another method is a mini-laparotomy, also known as a mini-tubal, which involves making a small incision in the abdomen just above the pubic hair line. The choice of method depends on various factors, including the patient's overall health, previous surgeries, and the surgeon's expertise.
Understanding Tubal Ligation
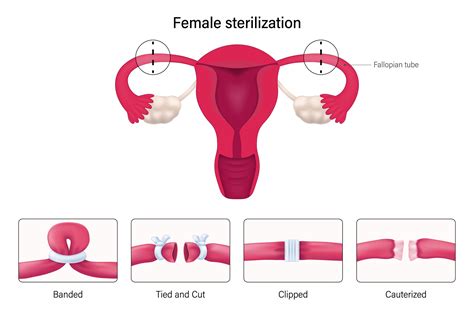
Tubal ligation is considered a safe procedure, but like any surgery, it carries risks and potential complications. These can include infection, bleeding, and unintended damage to surrounding organs. The procedure's success rate is high, but there is a small chance of failure, which can result in an ectopic pregnancy. This is a pregnancy in which a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube, and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Types of Tubal Ligation
There are several types of tubal ligation procedures, each with its own method of blocking the fallopian tubes. The most common methods include cutting and tying the tubes, using clips or rings to block the tubes, and sealing the tubes with an electric current. The choice of method depends on the surgeon's preference and the patient's individual situation.Benefits of Tubal Ligation
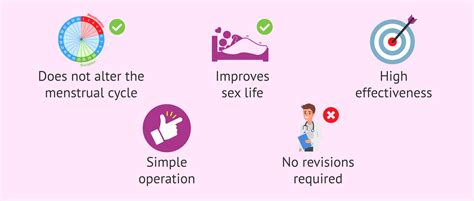
The benefits of tubal ligation are numerous. It is a highly effective method of birth control, with a very low failure rate. Once the procedure is done, it requires no further action to prevent pregnancy, unlike other birth control methods that require daily, weekly, or monthly maintenance. This makes it a convenient option for many women. Additionally, tubal ligation does not affect sexual pleasure or hormonal balance, as it does not involve the removal of any reproductive organs or the alteration of hormone production.
Effectiveness and Safety
The effectiveness of tubal ligation is well-documented, with studies showing that it is more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. Its safety profile is also favorable, with serious complications being rare. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks, including adverse reactions to anesthesia, infection, and injury to nearby organs.Preparation for Tubal Ligation

Preparation for tubal ligation involves several steps. Patients are typically advised to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, a few days before the procedure to minimize the risk of bleeding. They may also be asked to avoid eating and drinking for a certain period before the surgery. On the day of the procedure, patients will be given general anesthesia or regional anesthesia, such as a spinal block, to ensure they do not feel pain during the surgery.
Recovery After Tubal Ligation
Recovery after tubal ligation is generally quick, with most women able to return to their normal activities within a few days. However, it's recommended to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous exercise for about a week to allow the body to heal properly. Some women may experience mild side effects, such as abdominal pain, fatigue, and dizziness, but these typically resolve on their own within a short period.Risks and Complications
While tubal ligation is considered safe, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of. These can include infection, bleeding, and damage to the bowel or bladder. There is also a small risk of ectopic pregnancy if the procedure fails and a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. It's essential for women to discuss these risks with their healthcare provider and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any unusual symptoms after the procedure.
Reversal of Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation is considered a permanent form of birth control, but it is sometimes possible to reverse the procedure. The success of reversal depends on various factors, including the method used for the original tubal ligation, the length of the remaining fallopian tube segments, and the woman's age. Reversal is typically more successful in women who are under 40 years old and in those who have longer segments of their fallopian tubes remaining.Alternatives to Tubal Ligation
For women who desire permanent birth control but are hesitant about tubal ligation, there are alternatives to consider. One option is essure, a non-surgical procedure that involves inserting small metal coils into the fallopian tubes to block them. However, this method has been associated with significant side effects and is no longer widely used. Another option is a vasectomy for male partners, which is also a form of permanent birth control.
Male and Female Sterilization Comparison
When comparing male and female sterilization, several factors come into play. Vasectomy, the male sterilization procedure, is generally less invasive and has a quicker recovery time compared to tubal ligation. It also carries fewer risks and complications. However, the decision between the two ultimately depends on individual circumstances, including the couple's preferences, health status, and family planning goals.Counseling and Decision-Making

Counseling is a crucial step in the decision-making process for tubal ligation. Healthcare providers should discuss the procedure's benefits and risks, as well as alternatives, with the patient. It's essential for individuals to understand that tubal ligation is a permanent form of birth control and that the decision should not be taken lightly. Counseling can also help address any misconceptions or fears about the procedure.
Emotional and Psychological Aspects
The decision to undergo tubal ligation can have emotional and psychological implications. Some women may experience feelings of loss or grief after the procedure, especially if they had not completed their family or if the decision was made under pressure. It's important for women to have a support system and to discuss any emotional concerns with their healthcare provider or a counselor.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, tubal ligation is a highly effective and safe method of permanent birth control. While it carries potential risks and complications, the benefits for many women outweigh these considerations. It's crucial for individuals considering this procedure to be well-informed and to discuss their decision thoroughly with their healthcare provider. By understanding the procedure, its implications, and the alternatives available, women can make an informed decision that aligns with their reproductive goals and overall well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts, questions, or experiences regarding tubal ligation in the comments below. Your input can provide valuable insights and support to others who are considering this procedure. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this comprehensive guide to tubal ligation.
What is the success rate of tubal ligation?
+Tubal ligation is more than 99% effective in preventing pregnancy, making it a highly reliable form of permanent birth control.
Can tubal ligation be reversed?
+While tubal ligation is considered permanent, reversal is sometimes possible. The success of reversal depends on factors such as the method used for the original procedure, the length of the remaining fallopian tube segments, and the woman's age.
What are the potential risks and complications of tubal ligation?
+Potential risks and complications include infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding organs. There is also a small risk of ectopic pregnancy if the procedure fails.
