Intro
Discover the ultimate Umbilical Hernia Operation Guide, covering symptoms, diagnosis, repair surgery, and recovery, including laparoscopic and open hernia repair techniques, to help you understand and prepare for this common abdominal wall hernia treatment.
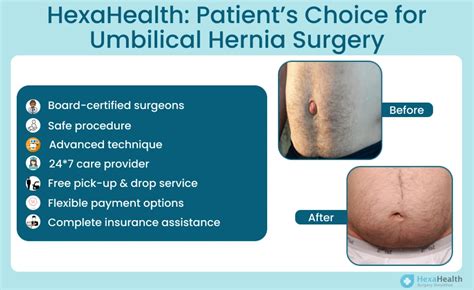
Umbilical hernias are a common health issue that can affect individuals of all ages, from infants to adults. An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the intestine or other abdominal tissue bulges through an opening in the abdominal muscles near the navel, also known as the belly button. This condition can be painful and may lead to complications if left untreated. Fortunately, an umbilical hernia operation can provide relief and prevent further problems. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of umbilical hernia operations, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, steps, and other key information related to the topic.
The importance of addressing umbilical hernias cannot be overstated. If left untreated, an umbilical hernia can lead to serious complications, such as strangulation, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is cut off, or incarceration, where the herniated tissue becomes trapped and cannot be pushed back into the abdomen. These complications can be life-threatening and require emergency medical attention. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical help if symptoms of an umbilical hernia persist or worsen over time.
Umbilical hernia operations are typically recommended for individuals who experience persistent pain, discomfort, or other symptoms associated with the condition. The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia, which means the patient will be asleep during the operation. The surgeon will make a small incision in the abdomen, usually near the navel, and gently push the herniated tissue back into place. The weakened area in the abdominal muscles is then reinforced with stitches or mesh to prevent future hernias.
Understanding Umbilical Hernia Operations

Umbilical hernia operations are a relatively common and safe procedure. However, as with any surgical operation, there are risks and potential complications involved. These may include infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. To minimize these risks, it is essential to choose a qualified and experienced surgeon who has performed numerous umbilical hernia operations.
Benefits of Umbilical Hernia Operations
The benefits of umbilical hernia operations are numerous. Some of the most significant advantages include: * Relief from pain and discomfort associated with the hernia * Prevention of complications, such as strangulation or incarceration * Improved quality of life, as individuals can engage in physical activities without worrying about the hernia * Reduced risk of future hernias, as the weakened area is reinforced with stitches or mesh * Minimal scarring, as the incision is typically small and discreetPreparation for Umbilical Hernia Operations
Preparation for an umbilical hernia operation typically begins several weeks before the scheduled procedure. Patients may be required to:
- Stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or anti-inflammatory drugs
- Avoid eating or drinking for a specified period before the operation
- Undergo pre-operative tests, such as blood work or imaging studies, to assess overall health
- Attend a pre-operative consultation with the surgeon to discuss the procedure, risks, and expected outcomes
Steps Involved in Umbilical Hernia Operations
The steps involved in an umbilical hernia operation may vary depending on the individual case and the surgeon's preferred technique. However, the general steps include: 1. Administration of general anesthesia to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure 2. Making a small incision in the abdomen, usually near the navel 3. Gently pushing the herniated tissue back into place 4. Reinforcing the weakened area with stitches or mesh to prevent future hernias 5. Closing the incision with sutures or staplesRecovery and Aftercare

Recovery and aftercare are crucial aspects of umbilical hernia operations. Patients can expect to:
- Experience some pain and discomfort, which can be managed with medication
- Have a dressing or bandage applied to the incision site to promote healing
- Be advised to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities for several weeks
- Attend follow-up appointments with the surgeon to monitor progress and remove sutures or staples
Risks and Complications
While umbilical hernia operations are generally safe, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of. These may include: * Infection, which can be treated with antibiotics * Bleeding or hematoma, which may require additional surgery * Adverse reactions to anesthesia, such as nausea or respiratory problems * Recurrence of the hernia, which may require further surgeryUmbilical Hernia Operation Costs and Insurance
The cost of an umbilical hernia operation can vary depending on factors such as location, surgeon's fees, and insurance coverage. In general, the procedure can range from $5,000 to $20,000 or more. It is essential to check with your insurance provider to determine the extent of coverage and any out-of-pocket expenses.
Choosing the Right Surgeon
Choosing the right surgeon for an umbilical hernia operation is critical to ensure a successful outcome. Some factors to consider when selecting a surgeon include: * Qualifications and experience in performing umbilical hernia operations * Reputation and patient reviews * Communication style and willingness to answer questions and address concerns * Hospital or surgical facility accreditation and reputationUmbilical Hernia Operation Alternatives

In some cases, alternatives to umbilical hernia operations may be considered. These may include:
- Watchful waiting, where the hernia is monitored for signs of complications
- Lifestyle changes, such as weight loss or avoiding heavy lifting
- Hernia trusses or support devices, which can help alleviate symptoms
Preventing Umbilical Hernias
Preventing umbilical hernias is not always possible, but there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk. These include: * Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the abdominal muscles * Avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activities * Engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the abdominal muscles * Eating a balanced diet to promote overall health and well-beingUmbilical Hernia Operation FAQs

What is an umbilical hernia operation?
+An umbilical hernia operation is a surgical procedure to repair a hernia that occurs near the navel.
What are the benefits of an umbilical hernia operation?
+The benefits of an umbilical hernia operation include relief from pain and discomfort, prevention of complications, and improved quality of life.
What are the risks and complications of an umbilical hernia operation?
+The risks and complications of an umbilical hernia operation include infection, bleeding, and adverse reactions to anesthesia.
In conclusion, an umbilical hernia operation is a safe and effective procedure for repairing hernias that occur near the navel. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, steps, and potential risks involved, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options. If you are experiencing symptoms of an umbilical hernia, it is essential to consult with a qualified surgeon to discuss the best course of treatment. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with umbilical hernia operations in the comments section below. Additionally, please feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this comprehensive guide.
