Intro
The West Nile virus has become a significant public health concern in recent years, with outbreaks reported in various parts of the world. As a mosquito-borne disease, it can cause severe symptoms, including fever, headaches, and in severe cases, neurological damage. Understanding the ways to treat West Nile virus is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications. In this article, we will delve into the different treatment options available for West Nile virus, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention.
The West Nile virus is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito, and the risk of infection is higher during peak mosquito season. While there is no specific vaccine available for humans, several treatment options can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. It is essential to note that treatment for West Nile virus is mainly focused on managing symptoms, as there is no cure for the disease.
As we explore the different treatment options, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of seeking medical attention immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term complications. In the following sections, we will discuss the various treatment options available for West Nile virus, including medication, therapy, and preventive measures.
Understanding West Nile Virus
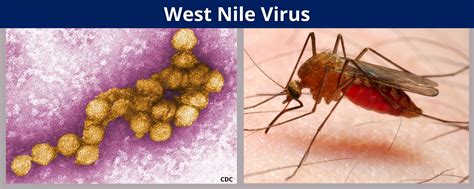
The symptoms of West Nile virus can range from mild to severe, with some individuals experiencing no symptoms at all. Common symptoms include fever, headaches, and body aches, while severe cases can lead to neurological damage, including meningitis and encephalitis. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Transmission and Risk Factors
The transmission of West Nile virus is primarily through the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected with the virus by feeding on birds that carry the virus, and then transmit the virus to humans through their bites. The risk of infection is higher during peak mosquito season, which typically occurs during the summer and early fall months.Certain individuals are at higher risk of infection, including older adults, young children, and people with weakened immune systems. It is essential to take preventive measures to reduce the risk of infection, including using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and eliminating standing water around the home.
Treatment Options for West Nile Virus
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, can help alleviate symptoms, including fever and headaches.
- Therapy: In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide supportive care, including intravenous fluids and respiratory support.
- Preventive measures: Taking preventive measures, such as using insect repellents and wearing protective clothing, can reduce the risk of infection.
It is essential to note that treatment for West Nile virus should only be administered under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Self-medication can lead to serious complications and worsen symptoms.
Medication and Therapy
Medication and therapy play a crucial role in managing symptoms and reducing the risk of complications. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, can help alleviate symptoms, including fever and headaches. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide supportive care, including intravenous fluids and respiratory support.Therapy, including physical therapy and occupational therapy, can help improve mobility and reduce the risk of long-term complications. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses specific needs and goals.
Preventive Measures

- Using insect repellents: Insect repellents, such as DEET and picaridin, can help reduce the risk of mosquito bites.
- Wearing protective clothing: Wearing protective clothing, including long-sleeved shirts and pants, can reduce the risk of mosquito bites.
- Eliminating standing water: Eliminating standing water around the home can reduce the risk of mosquito breeding and infection.
It is essential to take preventive measures seriously, as they can significantly reduce the risk of infection and prevent complications.
Public Health Strategies
Public health strategies play a crucial role in preventing and controlling West Nile virus outbreaks. The primary public health strategies include:- Surveillance: Surveillance programs can help monitor mosquito populations and detect early signs of infection.
- Education: Education campaigns can help raise awareness about the risks of West Nile virus and promote preventive measures.
- Control measures: Control measures, including insecticide spraying and larval control, can help reduce mosquito populations and prevent infection.
It is essential to work closely with public health officials to develop effective prevention and control strategies that address specific needs and goals.
Conclusion and Future Directions

As we move forward, it is essential to continue researching and developing new treatment options and preventive measures. This may include the development of vaccines, new medications, and innovative public health strategies. By staying informed and taking proactive steps, we can protect ourselves and our communities from the risks of West Nile virus.
Final Thoughts
In final thoughts, West Nile virus is a serious disease that requires prompt medical attention and effective treatment. By understanding the transmission dynamics, symptoms, and treatment options, we can develop effective prevention and control strategies that address specific needs and goals. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals and public health officials to reduce the risk of infection and prevent complications.We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with West Nile virus in the comments section below. Your feedback and insights can help raise awareness and promote preventive measures that can save lives.
What are the symptoms of West Nile virus?
+The symptoms of West Nile virus can range from mild to severe, with some individuals experiencing no symptoms at all. Common symptoms include fever, headaches, and body aches, while severe cases can lead to neurological damage, including meningitis and encephalitis.
How is West Nile virus transmitted?
+West Nile virus is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected with the virus by feeding on birds that carry the virus, and then transmit the virus to humans through their bites.
What are the treatment options for West Nile virus?
+Treatment for West Nile virus is mainly focused on managing symptoms, as there is no cure for the disease. The primary treatment options include medication, therapy, and preventive measures, such as using insect repellents and wearing protective clothing.
