Intro
Discover what health insurance covers, including medical expenses, hospital stays, and preventative care, with related benefits like dental, vision, and prescription coverage, to make informed decisions about your healthcare plan and coverage options.
Health insurance is a vital aspect of modern life, providing individuals and families with financial protection against unexpected medical expenses. With the rising costs of healthcare, having a comprehensive health insurance plan can be a lifesaver. But what exactly does health insurance cover? In this article, we will delve into the world of health insurance, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key aspects of coverage.
Health insurance is designed to provide coverage for a wide range of medical services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgical procedures, and prescription medications. The primary goal of health insurance is to ensure that individuals and families can access quality healthcare without incurring significant financial burdens. With the ever-increasing costs of medical care, health insurance has become an essential component of personal finance and healthcare planning.
The importance of health insurance cannot be overstated. Medical emergencies can arise at any time, and without adequate coverage, individuals and families may be forced to bear the full brunt of medical expenses. This can lead to financial ruin, as medical bills can quickly accumulate and become overwhelming. Health insurance provides a safety net, allowing individuals and families to focus on recovery and wellness rather than worrying about the financial implications of medical care.
Types of Health Insurance Coverage

There are several types of health insurance coverage, each with its own unique features and benefits. These include individual and family plans, group plans, Medicare and Medicaid, and short-term plans. Individual and family plans are designed for individuals and families who are not covered by an employer-sponsored plan. Group plans, on the other hand, are typically offered by employers as a benefit to their employees. Medicare and Medicaid are government-sponsored programs that provide coverage for seniors, low-income individuals, and families. Short-term plans, also known as temporary or gap insurance, provide limited coverage for a specified period, usually up to 12 months.
Individual and Family Plans
Individual and family plans are designed to provide comprehensive coverage for individuals and families who are not covered by an employer-sponsored plan. These plans can be purchased through the health insurance marketplace or directly from insurance companies. They typically offer a range of benefits, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgical procedures, and prescription medications. Some plans may also offer additional benefits, such as dental and vision coverage.Group Plans
Group plans are typically offered by employers as a benefit to their employees. These plans are designed to provide comprehensive coverage for employees and their families. Group plans often offer a range of benefits, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgical procedures, and prescription medications. They may also offer additional benefits, such as dental and vision coverage. Group plans are often more affordable than individual and family plans, as the cost is split among multiple employees.Benefits of Health Insurance

Health insurance provides numerous benefits, including financial protection, access to quality care, and preventive care. Financial protection is perhaps the most significant benefit of health insurance, as it provides individuals and families with a safety net against unexpected medical expenses. Access to quality care is another critical benefit, as health insurance enables individuals and families to access top-notch medical care without incurring significant financial burdens. Preventive care is also an essential benefit, as health insurance often covers routine check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations, which can help prevent illnesses and detect health problems early.
Some of the key benefits of health insurance include:
- Financial protection against unexpected medical expenses
- Access to quality medical care
- Preventive care, including routine check-ups and screenings
- Prescription medication coverage
- Hospital stay coverage
- Surgical procedure coverage
- Dental and vision coverage (in some plans)
Financial Protection
Financial protection is a critical aspect of health insurance, as it provides individuals and families with a safety net against unexpected medical expenses. Medical emergencies can arise at any time, and without adequate coverage, individuals and families may be forced to bear the full brunt of medical expenses. Health insurance helps to mitigate this risk, providing financial protection against unexpected medical expenses.Access to Quality Care
Access to quality care is another essential benefit of health insurance, as it enables individuals and families to access top-notch medical care without incurring significant financial burdens. Health insurance provides individuals and families with the freedom to choose their healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and specialists. This ensures that individuals and families can access quality care, regardless of their financial situation.How Health Insurance Works
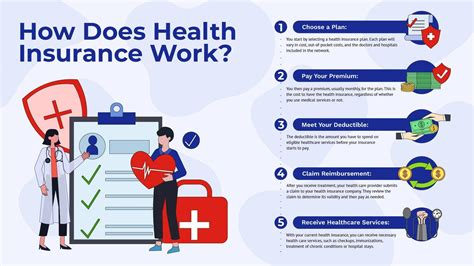
Health insurance works by providing individuals and families with financial protection against unexpected medical expenses. Here's a step-by-step guide to how health insurance works:
- Choose a plan: Individuals and families can choose a health insurance plan that meets their needs and budget.
- Pay premiums: Individuals and families pay premiums, which are typically monthly payments, to maintain their health insurance coverage.
- Receive coverage: In exchange for paying premiums, individuals and families receive coverage for a range of medical services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgical procedures, and prescription medications.
- Meet deductible: Individuals and families must meet their deductible, which is the amount they must pay out-of-pocket before their health insurance coverage kicks in.
- Pay copays and coinsurance: Individuals and families may be required to pay copays and coinsurance, which are payments made to healthcare providers for medical services.
Choosing a Plan
Choosing a health insurance plan can be a daunting task, as there are numerous options available. Individuals and families should consider their needs and budget when selecting a plan. Some factors to consider include: * **Network**: Does the plan have a strong network of healthcare providers? * **Coverage**: What medical services are covered under the plan? * **Cost**: What are the premiums, deductibles, copays, and coinsurance? * **Additional benefits**: Does the plan offer additional benefits, such as dental and vision coverage?Meeting Deductible
Meeting the deductible is an essential aspect of health insurance, as it requires individuals and families to pay a specified amount out-of-pocket before their coverage kicks in. The deductible can vary depending on the plan, but it's typically a fixed amount, such as $1,000 or $2,000. Once the deductible is met, individuals and families can access coverage for a range of medical services.Common Health Insurance Terms

Health insurance can be complex, with numerous terms and concepts to navigate. Here are some common health insurance terms:
- Premium: The monthly payment made to maintain health insurance coverage.
- Deductible: The amount individuals and families must pay out-of-pocket before their coverage kicks in.
- Copay: A payment made to healthcare providers for medical services.
- Coinsurance: A payment made to healthcare providers for medical services, usually a percentage of the total cost.
- Network: A group of healthcare providers who have contracted with the insurance company to provide medical services.
Premium
The premium is the monthly payment made to maintain health insurance coverage. Premiums can vary depending on the plan, age, health status, and other factors. Individuals and families should consider their budget when selecting a plan, as premiums can be a significant expense.Deductible
The deductible is the amount individuals and families must pay out-of-pocket before their coverage kicks in. Deductibles can vary depending on the plan, but they're typically a fixed amount, such as $1,000 or $2,000. Once the deductible is met, individuals and families can access coverage for a range of medical services.Health Insurance and Preventive Care

Health insurance plays a critical role in preventive care, as it provides individuals and families with access to routine check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations. Preventive care is essential for maintaining good health, as it can help prevent illnesses and detect health problems early. Health insurance typically covers a range of preventive care services, including:
- Routine check-ups: Regular check-ups with a primary care physician.
- Screenings: Tests and exams to detect health problems, such as cancer and diabetes.
- Vaccinations: Shots to prevent illnesses, such as flu and pneumonia.
Routine Check-ups
Routine check-ups are an essential aspect of preventive care, as they provide individuals and families with the opportunity to discuss their health with a primary care physician. Routine check-ups can help prevent illnesses and detect health problems early, reducing the risk of costly medical interventions.Screenings
Screenings are tests and exams that can help detect health problems, such as cancer and diabetes. Health insurance typically covers a range of screenings, including mammograms, colonoscopies, and blood tests. Screenings can help prevent illnesses and detect health problems early, reducing the risk of costly medical interventions.Health Insurance and Chronic Conditions

Health insurance plays a critical role in managing chronic conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and asthma. Chronic conditions require ongoing medical care, including prescription medications, doctor visits, and hospital stays. Health insurance can help individuals and families manage the costs of chronic conditions, providing access to quality care and reducing the risk of costly medical interventions.
Some common chronic conditions include:
- Diabetes: A condition characterized by high blood sugar levels.
- Heart disease: A condition characterized by narrowed or blocked arteries.
- Asthma: A condition characterized by inflammation and constriction of the airways.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Health insurance can help individuals and families manage the costs of diabetes, providing access to quality care, including prescription medications, doctor visits, and hospital stays.Heart Disease
Heart disease is a chronic condition characterized by narrowed or blocked arteries. Health insurance can help individuals and families manage the costs of heart disease, providing access to quality care, including prescription medications, doctor visits, and hospital stays.Health Insurance and Mental Health

Health insurance plays a critical role in mental health, providing individuals and families with access to quality care, including therapy, counseling, and prescription medications. Mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety, can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. Health insurance can help individuals and families manage the costs of mental health care, reducing the risk of costly medical interventions.
Some common mental health conditions include:
- Depression: A condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness.
- Anxiety: A condition characterized by persistent feelings of fear and anxiety.
- Bipolar disorder: A condition characterized by extreme mood swings.
Depression
Depression is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness. Health insurance can help individuals and families manage the costs of depression, providing access to quality care, including therapy, counseling, and prescription medications.Anxiety
Anxiety is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of fear and anxiety. Health insurance can help individuals and families manage the costs of anxiety, providing access to quality care, including therapy, counseling, and prescription medications.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, health insurance is a vital aspect of modern life, providing individuals and families with financial protection against unexpected medical expenses. With the rising costs of healthcare, having a comprehensive health insurance plan can be a lifesaver. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and key aspects of health insurance, individuals and families can make informed decisions about their healthcare needs.
If you're interested in learning more about health insurance or would like to explore your options, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with your friends and family. You can also visit our website for more information on health insurance and other related topics.
What is health insurance?
+Health insurance is a type of insurance that provides financial protection against unexpected medical expenses.
What are the benefits of health insurance?
+The benefits of health insurance include financial protection, access to quality care, and preventive care.
How does health insurance work?
+Health insurance works by providing individuals and families with financial protection against unexpected medical expenses. Individuals and families pay premiums, meet deductibles, and pay copays and coinsurance to access coverage.
What are the different types of health insurance?
+The different types of health insurance include individual and family plans, group plans, Medicare and Medicaid, and short-term plans.
How do I choose a health insurance plan?
+When choosing a health insurance plan, consider your needs and budget, as well as the plan's network, coverage, and cost.
