Intro
Discover what gallstones are, their symptoms, and treatment options. Learn about gallstone causes, types, and risks, including cholesterol stones and pigment stones, to understand this common gallbladder condition.
Gallstones are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. They are small, hard deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located under the liver that stores bile, a digestive fluid. Gallstones can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain, and can even lead to more serious complications if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the world of gallstones, exploring what they are, how they form, and what treatment options are available.
The formation of gallstones is a complex process that involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. One of the main causes of gallstones is an imbalance of bile salts, cholesterol, and bilirubin in the bile. When the bile becomes too concentrated, it can lead to the formation of small crystals that eventually grow into stones. Other factors that can increase the risk of developing gallstones include obesity, diabetes, and a diet high in fat and cholesterol.
Gallstones can be classified into two main types: cholesterol stones and pigment stones. Cholesterol stones are the most common type and are usually yellowish in color. They are made up of cholesterol and other substances and can range in size from small grains of sand to large pebbles. Pigment stones, on the other hand, are smaller and darker in color, and are made up of bilirubin and other substances. They are more common in people with certain medical conditions, such as cirrhosis of the liver or blood disorders.
Causes and Risk Factors

The causes and risk factors of gallstones are numerous and varied. As mentioned earlier, an imbalance of bile salts, cholesterol, and bilirubin in the bile is a major contributing factor. Other risk factors include a family history of gallstones, obesity, diabetes, and a diet high in fat and cholesterol. Certain medical conditions, such as cirrhosis of the liver or blood disorders, can also increase the risk of developing gallstones. Additionally, people who are older than 40, female, or of Native American or Mexican descent are more likely to develop gallstones.
Symptoms of Gallstones
Gallstones can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain. The most common symptom is biliary colic, which is a sudden and severe pain in the upper right abdomen that can radiate to the back or right shoulder. Other symptoms may include nausea and vomiting, fever, and jaundice, which is a yellowing of the skin and eyes. In some cases, gallstones may not cause any symptoms at all, and may only be discovered during a routine medical examination or imaging test.Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing gallstones typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests. The most common imaging test used to diagnose gallstones is ultrasound, which uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Other imaging tests, such as computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for gallstones usually involves surgery to remove the gallbladder, which is known as a cholecystectomy. This can be done using a minimally invasive surgical technique, known as laparoscopic surgery, or through a larger incision in the abdomen, known as open surgery. In some cases, medication may be used to dissolve the gallstones, but this is usually only effective for small stones and may take months or even years to work.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing gallstones involves making lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of developing them. This can include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet that is low in fat and cholesterol, and exercising regularly. Avoiding certain foods, such as fatty or greasy foods, and drinking plenty of water can also help to reduce the risk of gallstones. Additionally, people who are at high risk of developing gallstones, such as those with a family history or certain medical conditions, may need to take medication to reduce their risk.Complications of Gallstones
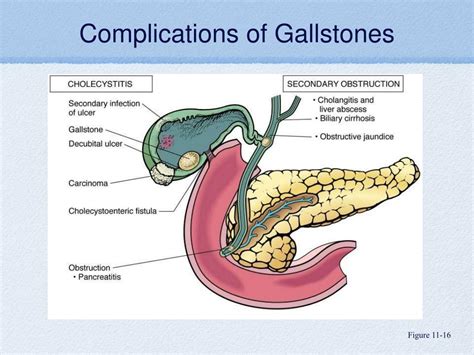
If left untreated, gallstones can lead to a range of complications, including inflammation of the gallbladder, known as cholecystitis, and blockage of the bile ducts, which can lead to jaundice and other serious health problems. In rare cases, gallstones can also increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
Gallstone Pancreatitis
Gallstone pancreatitis is a serious complication of gallstones that occurs when a gallstone blocks the bile duct and causes inflammation of the pancreas. This can lead to severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, and fever, and can even be life-threatening if left untreated. Treatment for gallstone pancreatitis usually involves hospitalization and administration of pain medication, as well as surgery to remove the gallbladder and any blockages in the bile ducts.Gallbladder Removal Surgery
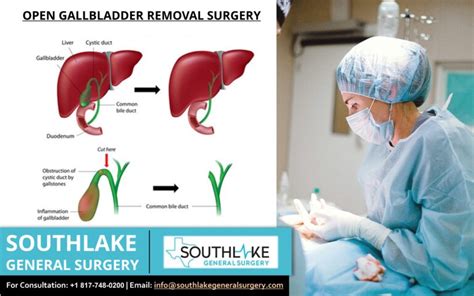
Gallbladder removal surgery, also known as cholecystectomy, is usually the recommended treatment for gallstones. The surgery can be done using a minimally invasive surgical technique, known as laparoscopic surgery, or through a larger incision in the abdomen, known as open surgery. The type of surgery used will depend on the individual's overall health and the severity of their symptoms.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery from gallbladder removal surgery usually takes several weeks, during which time the individual may need to follow a special diet and avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities. It is also important to follow the doctor's instructions for post-operative care, including taking pain medication and attending follow-up appointments.Diet and Nutrition

Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in the prevention and treatment of gallstones. Eating a balanced diet that is low in fat and cholesterol can help to reduce the risk of developing gallstones, while avoiding certain foods, such as fatty or greasy foods, can help to alleviate symptoms. Additionally, people who have had their gallbladder removed may need to follow a special diet to ensure proper digestion and nutrient absorption.
Foods to Eat and Avoid
There are several foods that can help to reduce the risk of gallstones, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Foods that are high in fat and cholesterol, such as fatty meats, dairy products, and processed snacks, should be avoided. Additionally, people who have had their gallbladder removed may need to avoid certain foods, such as fatty or greasy foods, and drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.Current Research and Developments

Current research and developments in the field of gallstones are focused on improving diagnosis and treatment options, as well as reducing the risk of complications. New imaging tests and surgical techniques are being developed to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of gallstone diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, researchers are studying the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to the development of gallstones, with the goal of developing new prevention and treatment strategies.
Future Directions
The future of gallstone research and treatment is promising, with new developments and advancements being made all the time. As our understanding of the causes and risk factors of gallstones improves, we can develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies. Additionally, advances in surgical techniques and imaging tests will continue to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of gallstone diagnosis and treatment.What are the symptoms of gallstones?
+The symptoms of gallstones can include severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, fever, and jaundice. In some cases, gallstones may not cause any symptoms at all.
How are gallstones diagnosed?
+Gallstones are usually diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans.
What is the treatment for gallstones?
+The treatment for gallstones usually involves surgery to remove the gallbladder, which is known as a cholecystectomy. In some cases, medication may be used to dissolve the gallstones.
Can gallstones be prevented?
+Yes, gallstones can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly. Avoiding certain foods, such as fatty or greasy foods, can also help to reduce the risk of gallstones.
What are the complications of gallstones?
+The complications of gallstones can include inflammation of the gallbladder, blockage of the bile ducts, and pancreatitis. In rare cases, gallstones can also increase the risk of developing pancreatic cancer.
In conclusion, gallstones are a common health issue that can cause a range of symptoms and complications. By understanding the causes and risk factors of gallstones, we can develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. If you suspect that you may have gallstones, it is essential to seek medical attention to prevent further complications. Remember to share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about gallstones and their treatment options.
