Intro
Discover the signs and symptoms of Adjustment Disorder, a stress-related condition. Learn about its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options, including therapy and coping mechanisms for emotional distress and mental health management.
Adjustment disorder is a mental health condition that occurs when an individual experiences significant emotional or behavioral difficulties in response to a specific stressor or stressful event. This condition is characterized by the development of emotional or behavioral symptoms in response to an identifiable stressor, which occurs within three months of the onset of the stressor. The symptoms or behavior are clinically significant as evidenced by either of the following: marked distress that is out of proportion to the severity or intensity of the stressor, significant impairment in social or occupational (academic) functioning.
The stressors that can trigger adjustment disorder can vary widely, including significant life changes, such as a move, job change, or the end of a relationship, as well as more severe stressors like the loss of a loved one, a natural disaster, or a serious illness. Adjustment disorder can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background, and its impact can be significant, affecting daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
Understanding adjustment disorder is crucial for providing appropriate support and treatment to those affected. It is a condition that is often misunderstood or overlooked, but recognizing its signs and symptoms can help individuals receive the help they need to cope with stressful events and improve their mental health. By exploring the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for adjustment disorder, individuals can better navigate the challenges of this condition and work towards recovery.
Types of Adjustment Disorder

There are several types of adjustment disorder, each with distinct characteristics and symptoms. These include:
- Adjustment disorder with depressed mood: characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities.
- Adjustment disorder with anxious mood: marked by feelings of anxiety, nervousness, and fear.
- Adjustment disorder with mixed anxiety and depressed mood: combines symptoms of both anxiety and depression.
- Adjustment disorder with disturbance of conduct: involves behavioral problems, such as vandalism, theft, or aggression.
- Adjustment disorder with mixed disturbance of emotions and conduct: combines emotional symptoms with behavioral problems. Understanding the specific type of adjustment disorder an individual is experiencing is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of adjustment disorder are complex and multifaceted, involving the interplay of various factors. These include:
- Significant life changes or stressors, such as a move, job change, or the end of a relationship.
- Traumatic events, such as the loss of a loved one, a natural disaster, or a serious illness.
- Personality traits, such as low self-esteem or a tendency to be overly self-critical.
- Lack of social support or a strong support network.
- History of mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety.
- Genetic predisposition to mental health conditions. Identifying the underlying causes and risk factors for adjustment disorder can help individuals and mental health professionals develop targeted interventions and support strategies.
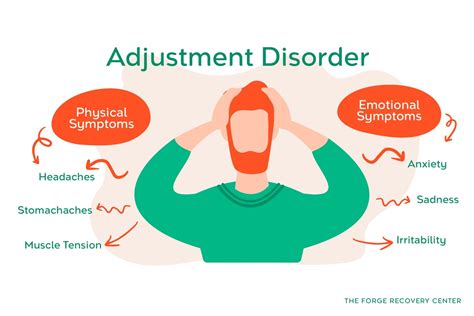
Symptoms of Adjustment Disorder
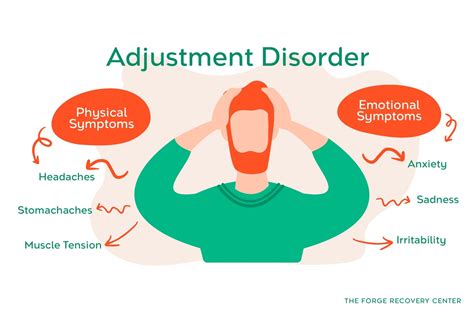
The symptoms of adjustment disorder can vary widely, depending on the individual and the specific stressor or event. Common symptoms include:
- Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities.
- Anxiety, nervousness, and fear.
- Behavioral problems, such as vandalism, theft, or aggression.
- Difficulty sleeping or changes in appetite.
- Fatigue or low energy.
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions.
- Avoidance of social interactions or activities. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for seeking help and support, as adjustment disorder can have a significant impact on daily life and overall well-being.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing adjustment disorder involves a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's symptoms, medical history, and mental health status. This may involve:
- A physical exam to rule out underlying medical conditions.
- A psychological evaluation to assess symptoms and mental health status.
- A review of the individual's medical and mental health history. Treatment for adjustment disorder typically involves a combination of psychotherapy and medication. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help individuals develop coping skills and strategies for managing stress and emotions. Medication, such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications, may be prescribed to help manage symptoms.
Coping Strategies and Support

Coping with adjustment disorder requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates self-care, social support, and professional help. Effective coping strategies include:
- Practicing self-care, such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
- Building a strong support network of friends, family, or support groups.
- Engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment.
- Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling.
- Developing healthy sleep habits and a balanced diet. By incorporating these coping strategies into daily life, individuals can better manage the symptoms of adjustment disorder and work towards recovery.
Prevention and Early Intervention

Preventing adjustment disorder or intervening early can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition. Strategies for prevention and early intervention include:
- Building a strong support network of friends, family, or support groups.
- Practicing self-care and stress management techniques.
- Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, at the first sign of symptoms.
- Developing healthy coping mechanisms and problem-solving skills.
- Encouraging open communication and emotional expression. By taking these steps, individuals can reduce their risk of developing adjustment disorder and promote overall mental health and well-being.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Adjustment disorder is a significant mental health condition that can have a profound impact on daily life and overall well-being. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for adjustment disorder, individuals can better navigate the challenges of this condition and work towards recovery. It is essential to seek help and support at the first sign of symptoms, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes. By incorporating self-care, social support, and professional help into daily life, individuals can manage the symptoms of adjustment disorder and promote overall mental health and well-being.What is adjustment disorder?
+Adjustment disorder is a mental health condition that occurs when an individual experiences significant emotional or behavioral difficulties in response to a specific stressor or stressful event.
What are the symptoms of adjustment disorder?
+The symptoms of adjustment disorder can vary widely, but common symptoms include feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities, anxiety, nervousness, and fear, and behavioral problems.
How is adjustment disorder diagnosed and treated?
+Diagnosing adjustment disorder involves a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's symptoms, medical history, and mental health status. Treatment typically involves a combination of psychotherapy and medication.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of adjustment disorder, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of adjustment disorder, we encourage you to seek help and support from a mental health professional. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
