Intro
Discover Aspartate Aminotransferase, an enzyme linked to liver health, AST levels, and alanine transaminase, crucial for diagnosing liver damage and disease.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of an individual. It performs a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion. One of the key enzymes found in the liver is aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AST. This enzyme is responsible for catalyzing the conversion of aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate to glutamate and oxaloacetate, a process that is essential for the proper functioning of the liver and other organs. In this article, we will delve into the world of aspartate aminotransferase, exploring its importance, functions, and the role it plays in maintaining optimal health.
Aspartate aminotransferase is an enzyme that is found in various tissues throughout the body, including the liver, heart, muscles, and kidneys. It is a transaminase, a type of enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from an amino acid to a keto acid. This process is essential for the production of energy and the synthesis of various biomolecules. AST is a cytosolic enzyme, meaning it is found in the cytoplasm of cells, and it plays a critical role in the metabolism of amino acids. The enzyme is composed of two subunits, a catalytic subunit and a cofactor subunit, which work together to facilitate the transfer of the amino group.
The importance of aspartate aminotransferase cannot be overstated. This enzyme is a vital component of the liver's detoxification process, helping to remove toxins and waste products from the body. It also plays a key role in the synthesis of glucose and other biomolecules, making it essential for maintaining optimal energy levels. In addition, AST is involved in the regulation of the body's acid-base balance, helping to maintain a stable pH level in the blood and other tissues. The enzyme is also used as a diagnostic tool, with elevated levels of AST in the blood often indicating liver damage or disease.
What is Aspartate Aminotransferase?
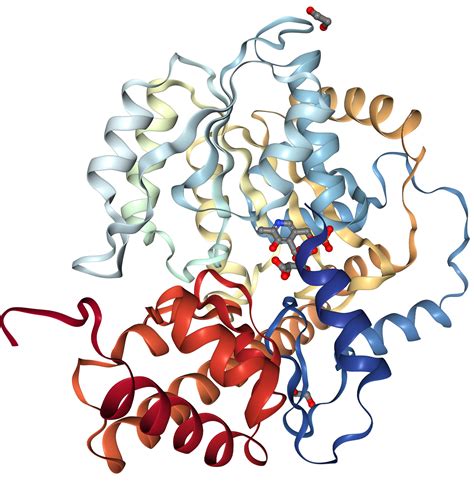
Functions of Aspartate Aminotransferase
The functions of aspartate aminotransferase are varied and complex. Some of the key functions of this enzyme include: * Catalyzing the transfer of an amino group from aspartate to alpha-ketoglutarate, resulting in the production of glutamate and oxaloacetate * Playing a critical role in the metabolism of amino acids, including the synthesis and degradation of these biomolecules * Helping to regulate the body's acid-base balance by removing excess ammonia from the blood and other tissues * Serving as a diagnostic tool, with elevated levels of AST in the blood often indicating liver damage or diseaseRole of Aspartate Aminotransferase in the Liver
Aspartate Aminotransferase and Liver Disease
Elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase in the blood can indicate liver damage or disease. This is because the enzyme is released into the bloodstream when liver cells are damaged, allowing it to be detected by laboratory tests. Some common causes of elevated AST levels include: * Hepatitis, a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver * Cirrhosis, a condition characterized by scarring of the liver tissue * Fatty liver disease, a condition in which excess fat builds up in the liver * Liver cancer, a type of cancer that affects the liver tissueAspartate Aminotransferase and Other Organs
Aspartate Aminotransferase and Disease
Elevated levels of aspartate aminotransferase can indicate disease or damage to various organs, including the liver, heart, and muscles. Some common causes of elevated AST levels include: * Myocardial infarction, a condition in which the heart muscle is damaged due to a lack of blood flow * Muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that affect the muscles * Kidney disease, a condition in which the kidneys are damaged or diseasedDiagnosis and Treatment of Aspartate Aminotransferase-Related Disorders

Treatment Options
Treatment options for aspartate aminotransferase-related disorders depend on the underlying cause of the elevated AST levels. Some common treatment options include: * Medications, such as antiviral medications or corticosteroids, which can help to reduce inflammation and promote healing * Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, which can help to promote overall health and well-being * Surgery, which may be necessary in some cases to repair or remove damaged tissuePrevention and Management of Aspartate Aminotransferase-Related Disorders

Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and treatment of aspartate aminotransferase-related disorders are critical for preventing long-term damage and promoting overall health and well-being. Some common benefits of early detection and treatment include: * Improved outcomes, which can help to prevent long-term damage and promote overall health and well-being * Reduced risk of complications, which can help to prevent long-term damage and promote overall health and well-being * Improved quality of life, which can help to promote overall health and well-beingWhat is aspartate aminotransferase?
+Aspartate aminotransferase is an enzyme that is found in various tissues throughout the body, including the liver, heart, muscles, and kidneys. It plays a critical role in the metabolism of amino acids and the synthesis of energy.
What are the functions of aspartate aminotransferase?
+The functions of aspartate aminotransferase include catalyzing the transfer of an amino group from aspartate to alpha-ketoglutarate, playing a critical role in the metabolism of amino acids, and helping to regulate the body's acid-base balance.
What are the causes of elevated aspartate aminotransferase levels?
+Elevated aspartate aminotransferase levels can be caused by a variety of factors, including liver damage or disease, heart damage or disease, and muscle damage or disease.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of aspartate aminotransferase and its role in maintaining optimal health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this important enzyme. By working together, we can promote overall health and well-being and reduce the risk of aspartate aminotransferase-related disorders.
