Intro
Discover 5 uses of Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, for managing hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias, with benefits for heart health, cardiovascular disease, and stroke prevention, offering therapeutic effects and medicinal applications.
The importance of understanding various medications and their uses cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to managing conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. One such medication is Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker that has been widely used for several decades. Its primary function is to relax the muscles of the heart and blood vessels, which in turn improves blood flow and reduces blood pressure. This makes it a critical drug for treating various cardiovascular conditions. The versatility of Diltiazem is evident in its multiple applications, ranging from the management of high blood pressure to controlling certain types of arrhythmias.
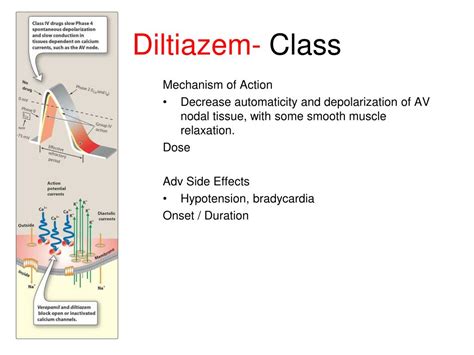
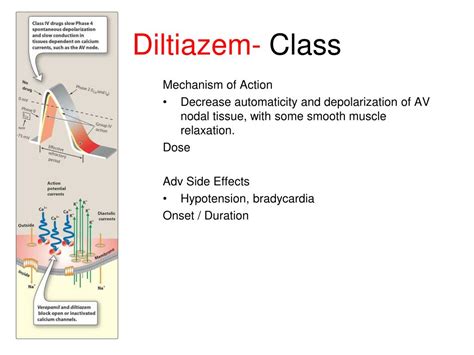
Diltiazem's mechanism of action is what makes it so effective in treating a variety of conditions. By blocking the entry of calcium into the muscle cells of the heart and arteries, it prevents the muscles from contracting too strongly. This action helps to lower blood pressure, reduce the heart's workload, and increase the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart. Its effects are not limited to these areas, as it also plays a role in managing and preventing certain types of chest pain (angina) and irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias). The drug's ability to be administered in different forms, including capsules, tablets, and injections, adds to its utility in clinical settings.
The application of Diltiazem in medical practice is diverse, reflecting its broad therapeutic benefits. It is often prescribed for patients with hypertension (high blood pressure), where it helps to reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney problems. Additionally, its use in managing angina pectoris (a condition characterized by chest pain due to reduced blood flow to the heart) is well established, as it increases blood flow to the heart muscle, reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks. Diltiazem's role in controlling certain types of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, underscores its importance in maintaining heart rhythm and preventing complications associated with irregular heartbeats.
Benefits of Diltiazem

Therapeutic Uses
Diltiazem's therapeutic uses are extensive, covering a range of cardiovascular conditions. It is commonly used for: - **Hypertension**: To lower high blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. - **Angina Pectoris**: To increase blood flow to the heart, thereby reducing chest pain. - **Arrhythmias**: Specifically, to control atrial fibrillation and flutter, helping to maintain a regular heart rhythm. - **Raynaud’s Phenomenon**: To improve blood flow to the fingers and toes, reducing the frequency and severity of episodes. - **Esophageal Spasm**: To relieve spasms of the esophagus, which can cause chest pain and difficulty swallowing.Working Mechanism
Administration and Dosage
The administration and dosage of Diltiazem can vary based on the condition being treated and the formulation of the drug. It is available in immediate-release and extended-release forms, with the latter providing a more sustained effect. The dosage is typically adjusted based on the patient's response to the medication, with regular monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate to ensure optimal therapeutic effects without adverse reactions. It's essential for patients to follow the prescribed dosage regimen and consult their healthcare provider before making any changes to their medication schedule.Side Effects and Precautions

Interactions with Other Medications
Diltiazem can interact with various medications, either by enhancing their effects or by increasing the risk of side effects. For instance, when used with beta-blockers, there is a risk of excessive bradycardia and heart block. Similarly, combining Diltiazem with other calcium channel blockers or certain anti-arrhythmic drugs can lead to additive effects, potentially resulting in hypotension or worsening heart failure. It's essential for healthcare providers to carefully review a patient's medication list before initiating Diltiazem therapy to minimize the risk of adverse interactions.Contraindications and Warnings
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The use of Diltiazem during pregnancy should be approached with caution, as there is limited data on its safety in pregnant women. It is classified as a Category C drug, meaning that while animal studies have shown adverse effects, there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. When used during breastfeeding, Diltiazem is secreted in breast milk, but the effect on the nursing infant is not known. Therefore, it is recommended that nursing mothers should either stop breastfeeding or stop taking Diltiazem, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.Overdose and Toxicity
Management of Overdose
The management of Diltiazem overdose requires prompt recognition and intervention. Healthcare providers should be vigilant for signs of toxicity and be prepared to implement appropriate therapeutic measures to mitigate the effects of the overdose. This includes monitoring the patient's vital signs closely and being prepared to provide advanced life support if necessary.Conclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Diltiazem in the comments below. Have you or a loved one used Diltiazem for a cardiovascular condition? What were your experiences, and how did the medication impact your quality of life? Your insights can provide valuable information and support to others who may be considering or currently using Diltiazem.
What is Diltiazem used for?
+Diltiazem is used to treat high blood pressure, control angina, and certain heart rhythm disorders.
How does Diltiazem work?
+Diltiazem works by blocking calcium channels, which helps to relax the muscles of the heart and blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
What are the common side effects of Diltiazem?
+Common side effects include dizziness, headache, nausea, and swelling of the feet, ankles, and hands.
