Intro
Discover the differences between DO vs MD degrees, including osteopathic vs allopathic medicine, medical school, and residency requirements, to make an informed decision about your medical career path.
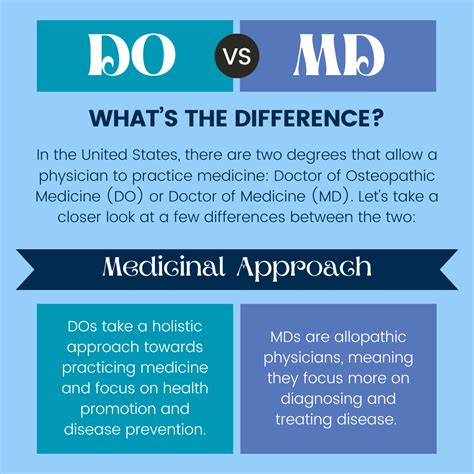
The debate between DO (Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine) and MD (Doctor of Medicine) has been ongoing for years, with many people wondering what the difference is between these two types of medical degrees. In the United States, both DOs and MDs are qualified to practice medicine, prescribe medications, and perform surgeries. However, there are some key differences between the two degrees that are worth exploring.
The main difference between DOs and MDs lies in their approach to medicine. DOs are trained to consider the whole person - mind, body, and spirit - when treating patients, while MDs tend to focus more on the symptoms and underlying causes of a disease. This difference in approach is reflected in the curriculum and training that DOs and MDs receive. DOs, for example, receive additional training in osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), which involves using manual techniques to diagnose and treat patients.
Another key difference between DOs and MDs is the type of residency programs they are eligible for. While both DOs and MDs can apply to the same residency programs, some programs may be more competitive for one or the other. Additionally, DOs may have an advantage when applying to osteopathic-focused residency programs.
Despite these differences, both DOs and MDs are qualified to provide high-quality medical care to their patients. In fact, many patients may not even notice a difference between the two types of doctors. Ultimately, the choice between a DO and an MD will depend on the individual patient's needs and preferences.
History of DO and MD Degrees
The history of the DO and MD degrees is complex and dates back to the late 19th century. The first osteopathic medical school was established in 1892 by Andrew Taylor Still, who believed that the conventional medical practices of the time were not effective in treating patients. Still developed a new approach to medicine that emphasized the importance of the musculoskeletal system and the use of manual techniques to diagnose and treat patients.
The MD degree, on the other hand, has a longer history that dates back to the Middle Ages. The first medical schools were established in Europe during the 12th century, and the MD degree became a standard qualification for medical practitioners. In the United States, the MD degree was first awarded in the late 18th century, and it quickly became the dominant medical degree in the country.
Curriculum and Training
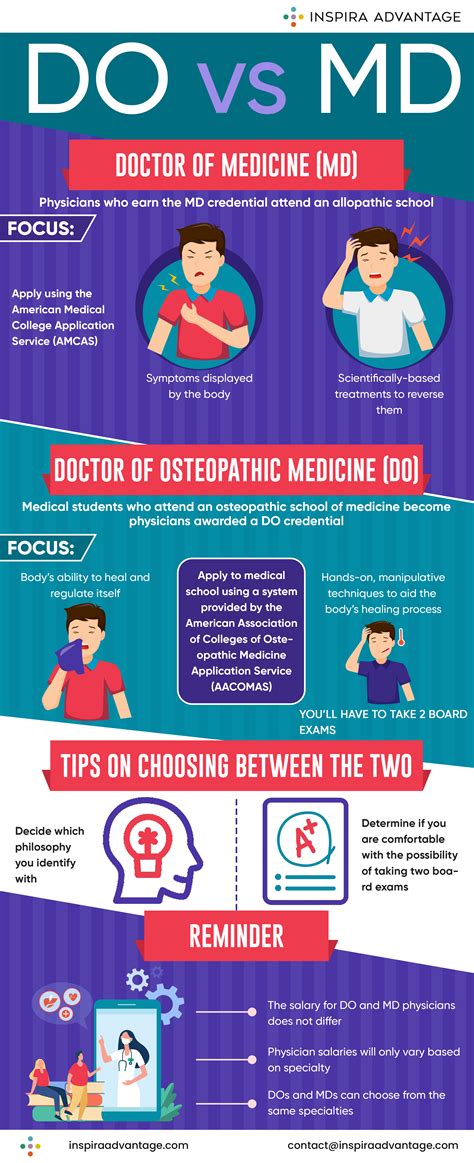
The curriculum and training for DOs and MDs are similar in many ways, but there are some key differences. Both DOs and MDs complete four years of medical school, followed by several years of residency training. However, DOs receive additional training in osteopathic principles and practices, including OMT.
The curriculum for DOs typically includes courses in:
- Osteopathic principles and practices
- Osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT)
- Pharmacology
- Pathology
- Physiology
- Anatomy
MDs, on the other hand, typically follow a more traditional curriculum that includes courses in:
- Pharmacology
- Pathology
- Physiology
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Microbiology

Residency Programs
Both DOs and MDs can apply to the same residency programs, but some programs may be more competitive for one or the other. DOs may have an advantage when applying to osteopathic-focused residency programs, while MDs may have an advantage when applying to more traditional residency programs.
Some popular residency programs for DOs include:
- Family medicine
- Internal medicine
- Pediatrics
- Obstetrics and gynecology
- Surgery
MDs, on the other hand, may be more likely to pursue residency programs in:
- Specialty fields like cardiology or gastroenterology
- Research-focused programs
- Academic medicine

Licensure and Certification
Both DOs and MDs must obtain licensure and certification to practice medicine. The process for obtaining licensure and certification is similar for both DOs and MDs, but there are some key differences.
DOs must pass the Comprehensive Osteopathic Medical Licensing Examination (COMLEX) series, which consists of four levels of exams. MDs, on the other hand, must pass the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) series, which consists of four levels of exams.
In addition to passing the licensing exams, both DOs and MDs must also obtain certification in their specialty field. Certification is typically obtained through a professional organization, such as the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) or the American Osteopathic Board of Internal Medicine (AOBIM).

Specialty Certification
Both DOs and MDs can obtain specialty certification in a variety of fields, including:
- Internal medicine
- Family medicine
- Pediatrics
- Obstetrics and gynecology
- Surgery
The process for obtaining specialty certification typically involves passing a certification exam and completing a certain number of years of practice in the specialty field.

Practice and Patient Care
Both DOs and MDs are qualified to provide high-quality medical care to their patients. However, there are some key differences in the way that DOs and MDs approach patient care.
DOs are trained to consider the whole person - mind, body, and spirit - when treating patients. This approach is reflected in the use of OMT and other osteopathic techniques to diagnose and treat patients.
MDs, on the other hand, tend to focus more on the symptoms and underlying causes of a disease. This approach is reflected in the use of pharmaceuticals and other traditional medical treatments.

Patient Satisfaction
Studies have shown that patients are generally satisfied with the care they receive from both DOs and MDs. However, some studies have suggested that patients may be more satisfied with the care they receive from DOs, particularly in terms of communication and empathy.
A study published in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association found that patients who received care from DOs reported higher levels of satisfaction with their care, particularly in terms of communication and empathy.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the debate between DOs and MDs is complex and multifaceted. While both types of medical degrees have their advantages and disadvantages, the choice between a DO and an MD will ultimately depend on the individual patient's needs and preferences.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, it is likely that the role of DOs and MDs will continue to change. However, one thing is certain - both DOs and MDs are qualified to provide high-quality medical care to their patients, and patients can feel confident in the care they receive from either type of doctor.

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with DOs and MDs in the comments below. Have you had a positive experience with a DO or MD? Do you have any questions about the differences between these two types of medical degrees? Let us know, and we'll do our best to provide you with the information you need.
What is the main difference between a DO and an MD?
+The main difference between a DO and an MD is the approach to medicine. DOs are trained to consider the whole person - mind, body, and spirit - when treating patients, while MDs tend to focus more on the symptoms and underlying causes of a disease.
Can DOs and MDs practice in the same fields?
+Yes, DOs and MDs can practice in the same fields. Both types of doctors can work in primary care, specialty fields, and research.
Is one type of degree better than the other?
+No, one type of degree is not inherently better than the other. The choice between a DO and an MD will depend on the individual patient's needs and preferences.
