Intro
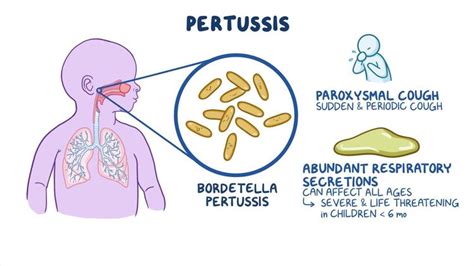
Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. It is a significant public health concern, particularly among infants and young children, as it can lead to severe complications and even death. The disease is characterized by a distinctive cough that sounds like a "whoop," which is often accompanied by vomiting, exhaustion, and other symptoms. Pertussis is spread through respiratory droplets, such as those produced by coughing or sneezing, and can be prevented through vaccination.
The importance of understanding pertussis cannot be overstated, as it is a serious disease that can have devastating consequences if left untreated. In recent years, there has been a resurgence of pertussis cases in many parts of the world, highlighting the need for continued vigilance and education about the disease. By learning more about pertussis, its symptoms, treatment options, and prevention methods, individuals can take steps to protect themselves and their loved ones from this potentially deadly illness.
Pertussis is a significant concern for parents, healthcare professionals, and public health officials, as it can spread quickly and easily among vulnerable populations. The disease can cause serious complications, such as pneumonia, bronchiolitis, and encephalopathy, particularly among infants and young children. Furthermore, pertussis can have a significant impact on quality of life, causing missed school or work days, decreased productivity, and increased healthcare costs. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of pertussis, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce the risk of infection and promote overall health and well-being.
What is Pertussis?

Symptoms of Pertussis
The symptoms of pertussis can vary depending on the age and health status of the individual. Infants and young children are at highest risk of developing severe symptoms, which can include: * A distinctive cough that sounds like a "whoop" * Vomiting after coughing * Exhaustion * Loss of appetite * Fever * Apnea (pauses in breathing) * Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the skin)In older children and adults, the symptoms of pertussis may be milder and can include:
- A dry, hacking cough
- Mild fever
- Sore throat
- Runny nose
- Fatigue
Causes and Risk Factors
Diagnosis and Treatment
Pertussis is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common diagnostic tests for pertussis include: * Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test: This test detects the presence of pertussis DNA in respiratory secretions * Culture test: This test detects the presence of pertussis bacteria in respiratory secretions * Serology test: This test detects the presence of pertussis antibodies in the bloodTreatment for pertussis typically involves a combination of antibiotics and supportive care. Antibiotics, such as azithromycin or clarithromycin, can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms, as well as prevent the spread of the disease to others. Supportive care, such as rest, hydration, and nutrition, can help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
Prevention and Vaccination

In addition to vaccination, several other measures can help prevent the spread of pertussis, including:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick
- Avoiding sharing food, drinks, or utensils with individuals who are sick
- Staying home from work or school when sick
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who are at high risk of developing severe pertussis, such as infants and young children
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Pertussis can cause several complications, particularly among infants and young children. Some of the most common complications include: * Pneumonia: A bacterial infection of the lungs that can cause severe respiratory symptoms and even death * Bronchiolitis: An inflammation of the small airways that can cause wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing * Encephalopathy: A brain disorder that can cause seizures, coma, and even death * Apnea: Pauses in breathing that can lead to respiratory failure and even deathIn addition to these complications, pertussis can also have long-term effects on an individual's health and well-being. Some of the most common long-term effects include:
- Chronic cough: A persistent cough that can last for weeks or even months after recovery
- Fatigue: A feeling of exhaustion and weakness that can last for weeks or even months after recovery
- Sleep disturbances: Difficulty sleeping or insomnia that can last for weeks or even months after recovery
What are the symptoms of pertussis?
+The symptoms of pertussis can include a distinctive cough that sounds like a "whoop," vomiting after coughing, exhaustion, loss of appetite, fever, apnea, and cyanosis.
How is pertussis diagnosed?
+Pertussis is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as PCR, culture, and serology tests.
How can pertussis be prevented?
+The most effective way to prevent pertussis is through vaccination. Additional measures, such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and staying home from work or school when sick, can also help prevent the spread of the disease.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of pertussis, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By taking proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones from this potentially deadly disease, you can help promote overall health and well-being. If you have any further questions or concerns about pertussis, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others. Together, we can work to reduce the risk of pertussis and create a healthier, safer community for everyone.
