Intro
Discover 5 key facts about the Antinuclear Antibody Test, including its role in diagnosing autoimmune diseases like Lupus and Rheumatoid Arthritis, and understanding ANA test results and titers.
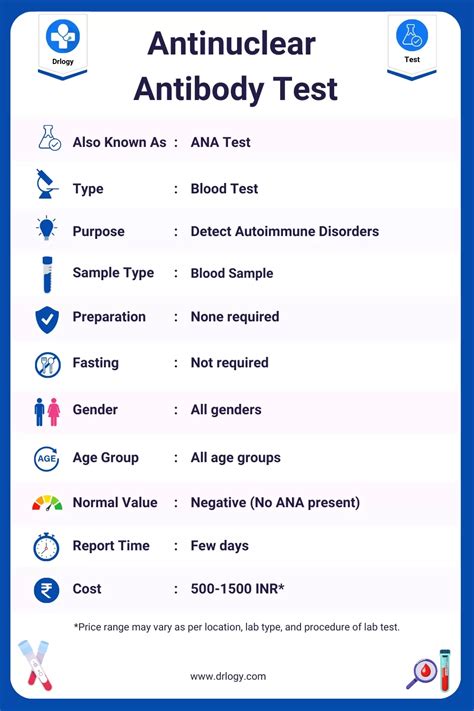
The antinuclear antibody (ANA) test has become a crucial diagnostic tool in the medical field, particularly in the detection of autoimmune diseases. This test measures the levels of antinuclear antibodies in the blood, which are proteins that the immune system produces to fight off foreign substances. However, in the case of autoimmune diseases, these antibodies mistakenly target the body's own tissues, leading to inflammation and damage. Understanding the ANA test is essential for individuals who may be experiencing symptoms of autoimmune diseases, as well as for healthcare professionals seeking to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
The importance of the ANA test cannot be overstated, as it has revolutionized the way doctors diagnose and manage autoimmune diseases. By detecting the presence of antinuclear antibodies, healthcare professionals can identify individuals who are at risk of developing these conditions and provide prompt treatment to prevent long-term damage. Moreover, the ANA test has also enabled researchers to better understand the underlying mechanisms of autoimmune diseases, leading to the development of new therapies and treatments. As research continues to uncover the complexities of autoimmune diseases, the ANA test remains a vital tool in the diagnosis and management of these conditions.
The ANA test is particularly useful in diagnosing diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma, which are characterized by the presence of antinuclear antibodies. However, it is essential to note that a positive ANA test result does not necessarily mean that an individual has an autoimmune disease. Rather, it indicates the presence of antinuclear antibodies, which can be found in individuals with and without autoimmune diseases. Therefore, a comprehensive diagnosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and laboratory tests, including the ANA test.
What is the Antinuclear Antibody Test?

How is the Antinuclear Antibody Test Performed?
The ANA test is performed using a technique called indirect immunofluorescence, which involves adding the individual's blood sample to a slide containing human cells. The slide is then incubated, and the presence of antinuclear antibodies is detected using a fluorescent dye. The results of the test are typically reported as a titer, which indicates the level of antinuclear antibodies present in the blood. A positive ANA test result is usually reported as a titer of 1:80 or higher, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the specific test used.What do the Results of the Antinuclear Antibody Test Mean?
What are the Benefits of the Antinuclear Antibody Test?
The ANA test has several benefits, including: * Early detection of autoimmune diseases, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of long-term damage * Accurate diagnosis of autoimmune diseases, enabling healthcare professionals to develop effective treatment plans * Monitoring of disease activity and response to treatment * Identification of individuals who are at risk of developing autoimmune diseases, enabling preventive measures to be takenWhat are the Limitations of the Antinuclear Antibody Test?

How is the Antinuclear Antibody Test Used in Clinical Practice?
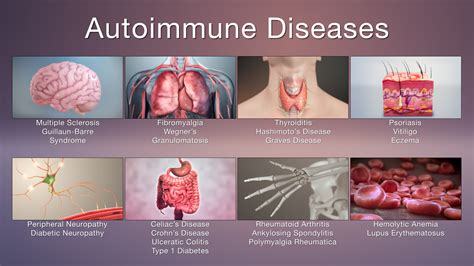
The ANA test is widely used in clinical practice to diagnose and manage autoimmune diseases. It is typically used in combination with other laboratory tests and clinical evaluation to confirm a diagnosis. The test is also used to monitor disease activity and response to treatment, enabling healthcare professionals to adjust treatment plans as needed.What are the Common Autoimmune Diseases Diagnosed using the Antinuclear Antibody Test?
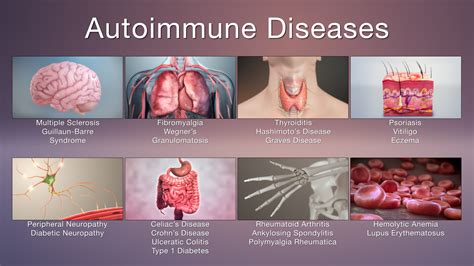
What are the Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases?
The symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary depending on the specific disease and the individual affected. Common symptoms include: * Joint pain and inflammation * Fatigue * Skin rashes * Hair loss * Mouth sores * Fever * Weight lossHow are Autoimmune Diseases Treated?
What is the Prognosis for Individuals with Autoimmune Diseases?
The prognosis for individuals with autoimmune diseases can vary depending on the specific disease and the individual affected. With prompt treatment and lifestyle modifications, many individuals with autoimmune diseases can manage their symptoms and prevent long-term damage. However, some autoimmune diseases can be life-threatening if left untreated or if treatment is delayed.Conclusion and Future Directions
What is the antinuclear antibody test used for?
+The antinuclear antibody test is used to diagnose and manage autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and scleroderma.
What are the benefits of the antinuclear antibody test?
+The benefits of the antinuclear antibody test include early detection of autoimmune diseases, accurate diagnosis, and monitoring of disease activity and response to treatment.
What are the limitations of the antinuclear antibody test?
+The limitations of the antinuclear antibody test include false-positive and false-negative results, variability in test results, and limited sensitivity and specificity.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the antinuclear antibody test and its role in diagnosing and managing autoimmune diseases. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may find it useful. Additionally, we encourage you to take action by consulting with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing symptoms of an autoimmune disease or if you have any concerns about your health.
