Intro
Learn about Tetanus Booster Injection, including symptoms, vaccination schedules, and side effects, to protect against Tetanus infection and ensure timely booster shots for optimal immunity and health.
Tetanus is a serious bacterial infection that can cause muscle stiffness, spasms, and rigidity, and can be life-threatening if left untreated. The tetanus booster injection is a crucial vaccine that helps prevent tetanus infection by boosting the body's immunity against the tetanus toxin. In this article, we will delve into the world of tetanus booster injections, exploring their importance, benefits, and everything you need to know about getting vaccinated.
The tetanus booster injection is a widely recommended vaccine that is essential for individuals of all ages. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that adults receive a tetanus booster shot every 10 years, while children should receive a series of tetanus vaccinations as part of their routine immunization schedule. The tetanus booster injection is particularly important for individuals who work with soil, dust, or dirt, as these environments are common breeding grounds for tetanus bacteria.
Tetanus infections can be devastating, and the consequences of not getting vaccinated can be severe. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), tetanus is responsible for approximately 50,000 to 100,000 deaths worldwide each year. In the United States alone, the CDC reports that there are approximately 30 to 40 reported cases of tetanus each year, with a mortality rate of around 10%. The importance of getting vaccinated against tetanus cannot be overstated, and it is crucial that individuals take proactive steps to protect themselves against this deadly infection.
What is Tetanus?
Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani, a type of bacteria that is commonly found in soil, dust, and dirt. The bacteria produce a toxin that can cause muscle stiffness, spasms, and rigidity, and can lead to respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and even death. Tetanus infections can occur through wounds or cuts that become contaminated with tetanus bacteria, and can also be spread through contaminated food or water.
Types of Tetanus Infections
There are several types of tetanus infections, including: * Generalized tetanus: This is the most common type of tetanus infection, which affects the entire body. * Localized tetanus: This type of infection is limited to a specific area of the body, such as a wound or cut. * Cephalic tetanus: This is a rare type of tetanus infection that affects the head and face. * Neonatal tetanus: This is a type of tetanus infection that occurs in newborn babies, typically within the first few weeks of life.Benefits of Tetanus Booster Injections

The tetanus booster injection offers numerous benefits, including:
- Prevention of tetanus infection: The most significant benefit of the tetanus booster injection is that it helps prevent tetanus infection by boosting the body's immunity against the tetanus toxin.
- Reduced risk of complications: By preventing tetanus infection, the tetanus booster injection can also reduce the risk of complications, such as respiratory failure, cardiac arrest, and death.
- Protection against other diseases: Some tetanus vaccines, such as the Tdap vaccine, also offer protection against other diseases, such as diphtheria and pertussis.
- Long-term immunity: The tetanus booster injection can provide long-term immunity against tetanus, with some studies suggesting that it can last for up to 10 years or more.
Who Should Get the Tetanus Booster Injection?
The tetanus booster injection is recommended for individuals of all ages, including: * Adults: Adults should receive a tetanus booster shot every 10 years, or sooner if they have a deep or dirty wound. * Children: Children should receive a series of tetanus vaccinations as part of their routine immunization schedule. * Pregnant women: Pregnant women should receive a Tdap vaccine during the third trimester of pregnancy to protect themselves and their newborn babies against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis. * Individuals with certain medical conditions: Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, may be at increased risk of tetanus infection and should receive a tetanus booster injection as recommended by their healthcare provider.How the Tetanus Booster Injection Works

The tetanus booster injection works by introducing a small amount of tetanus toxin into the body, which stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against the toxin. These antibodies help to protect the body against tetanus infection by neutralizing the toxin and preventing it from causing damage.
Types of Tetanus Vaccines
There are several types of tetanus vaccines available, including: * Td vaccine: This vaccine protects against tetanus and diphtheria. * Tdap vaccine: This vaccine protects against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis. * DTaP vaccine: This vaccine protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis, and is typically given to children under the age of 7.Side Effects of the Tetanus Booster Injection

While the tetanus booster injection is generally safe and well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, including:
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site
- Fatigue or tiredness
- Headache or muscle pain
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever or chills
Contraindications of the Tetanus Booster Injection
The tetanus booster injection is contraindicated in individuals who: * Have a history of severe allergic reaction to the vaccine or its components * Have a weakened immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS or cancer * Are taking certain medications, such as immunosuppressants or chemotherapyPreparation for the Tetanus Booster Injection

To prepare for the tetanus booster injection, individuals should:
- Inform their healthcare provider of any medical conditions or allergies
- Discuss any concerns or questions with their healthcare provider
- Avoid taking certain medications, such as immunosuppressants or chemotherapy, before receiving the vaccine
- Plan to rest and avoid strenuous activities after receiving the vaccine
What to Expect After the Tetanus Booster Injection
After receiving the tetanus booster injection, individuals may experience some side effects, such as pain or redness at the injection site. It is essential to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare provider and to seek medical attention if any severe side effects occur.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
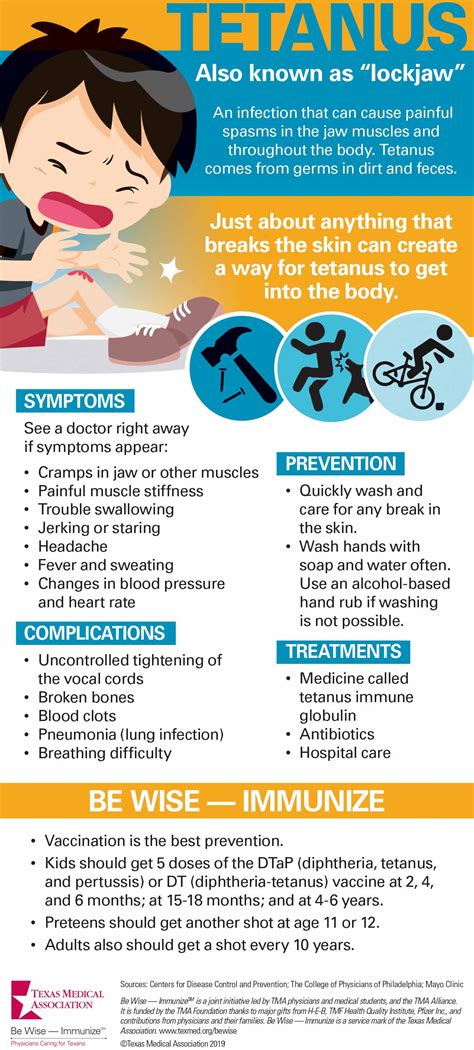
In conclusion, the tetanus booster injection is a crucial vaccine that helps prevent tetanus infection by boosting the body's immunity against the tetanus toxin. It is essential for individuals of all ages to receive the tetanus booster injection as recommended by their healthcare provider to protect themselves against this deadly infection. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and potential side effects of the tetanus booster injection, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take proactive steps to prevent tetanus infection.
What is the recommended schedule for tetanus booster injections?
+The recommended schedule for tetanus booster injections is every 10 years for adults, and as part of the routine immunization schedule for children.
Can I get tetanus from a minor cut or scratch?
+Yes, it is possible to get tetanus from a minor cut or scratch if the wound becomes contaminated with tetanus bacteria.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with the tetanus booster injection?
+Yes, the tetanus booster injection can cause some side effects, such as pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, fatigue, headache, or muscle pain.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to tetanus booster injections. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Remember to share this article with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of tetanus vaccination. Together, we can work towards preventing tetanus infection and promoting public health.
