Intro
Discover the Full Blood Count definition, a medical test analyzing blood components, including red and white blood cell count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, to diagnose conditions like anemia, infection, and inflammation, using key parameters like CBC and differential count.
A full blood count, also known as a complete blood count, is a crucial diagnostic tool used to evaluate the overall health of an individual. It is a common blood test that provides valuable information about the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This test is often used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions, from anemia and infections to blood disorders and cancer. In this article, we will delve into the world of full blood counts, exploring their importance, components, and implications for our health.
The full blood count is a vital test that helps healthcare professionals understand the underlying causes of various symptoms and diseases. By analyzing the different components of blood, doctors can identify abnormalities, diagnose conditions, and develop effective treatment plans. For instance, a full blood count can help diagnose anemia, a condition characterized by low red blood cell count, or identify infections, such as sepsis, which can cause an elevated white blood cell count. Moreover, this test can also detect blood disorders, such as leukemia, and monitor the progression of diseases, like cancer.
The importance of full blood counts cannot be overstated, as they provide a comprehensive overview of our blood's composition and function. By examining the different components of blood, healthcare professionals can gain insights into our overall health, identify potential health risks, and develop personalized treatment plans. In the following sections, we will explore the components of a full blood count, their functions, and the implications of abnormal results.
Components of a Full Blood Count
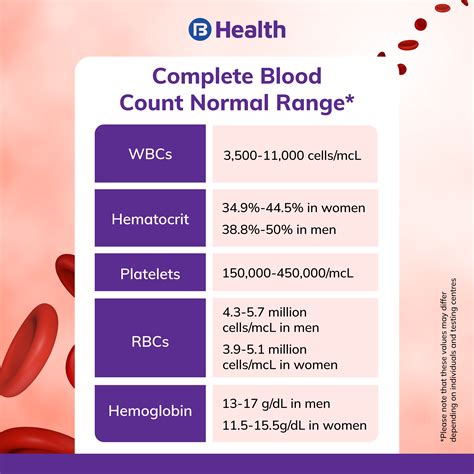
A full blood count typically includes several components, each providing valuable information about our blood's composition and function. The main components of a full blood count are:
- Red blood cell count: measures the number of red blood cells in the blood
- White blood cell count: measures the number of white blood cells in the blood
- Platelet count: measures the number of platelets in the blood
- Hemoglobin: measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood
- Hematocrit: measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood
- Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): measures the average size of red blood cells
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH): measures the average amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells
- Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC): measures the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells
Each of these components plays a crucial role in our overall health, and abnormalities in any of these areas can indicate underlying health issues.
Red Blood Cell Count
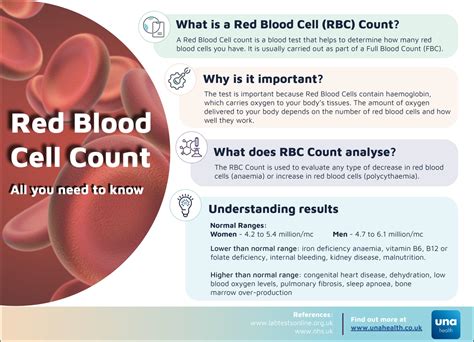
The red blood cell count is an essential component of a full blood count, as it measures the number of red blood cells in the blood. Red blood cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. A low red blood cell count, also known as anemia, can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. On the other hand, a high red blood cell count can indicate dehydration, polycythemia vera, or other underlying health conditions.
Functions of Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells play a vital role in our overall health, and their functions include:
- Carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues
- Carrying carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs
- Regulating blood pH levels
- Maintaining blood viscosity
Abnormalities in red blood cell count or function can indicate underlying health issues, such as anemia, blood disorders, or chronic diseases.
White Blood Cell Count
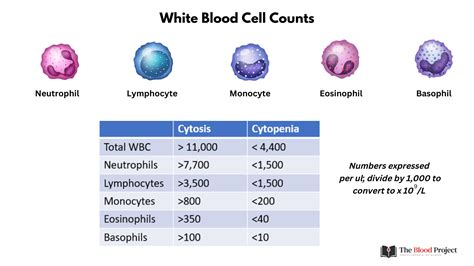
The white blood cell count is another crucial component of a full blood count, as it measures the number of white blood cells in the blood. White blood cells are part of the immune system and play a vital role in fighting infections and diseases. A low white blood cell count, also known as leukopenia, can increase the risk of infections, while a high white blood cell count can indicate inflammation, infection, or underlying health conditions, such as leukemia.
Functions of White Blood Cells
White blood cells play a vital role in our overall health, and their functions include:
- Fighting infections and diseases
- Regulating inflammation
- Maintaining immune system function
- Removing foreign substances from the body
Abnormalities in white blood cell count or function can indicate underlying health issues, such as infections, blood disorders, or chronic diseases.
Platelet Count

The platelet count is an essential component of a full blood count, as it measures the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets are small blood cells that play a crucial role in blood clotting and preventing bleeding. A low platelet count, also known as thrombocytopenia, can increase the risk of bleeding, while a high platelet count can indicate underlying health conditions, such as thrombocythemia or blood disorders.
Functions of Platelets
Platelets play a vital role in our overall health, and their functions include:
- Forming blood clots to prevent bleeding
- Regulating blood clotting
- Maintaining blood vessel integrity
- Removing foreign substances from the body
Abnormalities in platelet count or function can indicate underlying health issues, such as bleeding disorders, blood disorders, or chronic diseases.
Interpretation of Full Blood Count Results
Interpreting full blood count results requires a comprehensive understanding of the different components and their functions. Healthcare professionals use full blood count results to diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions, from anemia and infections to blood disorders and cancer. Abnormal results can indicate underlying health issues, and prompt treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Common Abnormalities
Common abnormalities in full blood count results include:
- Anemia: low red blood cell count or low hemoglobin levels
- Leukopenia: low white blood cell count
- Thrombocytopenia: low platelet count
- Polycythemia vera: high red blood cell count
- Thrombocythemia: high platelet count
- Leukemia: abnormal white blood cell count
Abnormalities in full blood count results can indicate underlying health issues, and prompt treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
FAQs
What is a full blood count?
+A full blood count is a blood test that measures the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Why is a full blood count important?
+A full blood count is important because it provides valuable information about our overall health, helps diagnose and monitor health conditions, and guides treatment decisions.
What are the components of a full blood count?
+The components of a full blood count include red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration.
In conclusion, a full blood count is a vital diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about our overall health. By understanding the different components of a full blood count and their functions, healthcare professionals can diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions, from anemia and infections to blood disorders and cancer. If you have any questions or concerns about full blood counts or your health in general, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with your friends and family. Remember, knowledge is power, and staying informed about our health is the first step towards maintaining overall well-being.
