Intro
Discover the ideal glucose fasting range for optimal health, including normal blood sugar levels, glucose tolerance, and insulin sensitivity to manage diabetes and metabolic syndrome effectively.
Maintaining a healthy glucose level is crucial for overall well-being, and understanding the glucose fasting range is essential for individuals who want to monitor their blood sugar levels. The glucose fasting range refers to the normal range of blood glucose levels after an overnight fast, typically 8-12 hours. This range is used as a benchmark to diagnose and manage diabetes, as well as to assess the risk of developing insulin resistance and other metabolic disorders. In this article, we will delve into the importance of glucose fasting range, its benefits, and how it can be used to improve overall health.
The glucose fasting range is a critical indicator of glucose metabolism, and abnormal levels can indicate underlying health issues. For instance, high fasting glucose levels can be a sign of insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. On the other hand, low fasting glucose levels can be a sign of hypoglycemia, which can be caused by various factors, including medication, hormonal imbalances, or certain medical conditions. Understanding the glucose fasting range can help individuals take proactive steps to manage their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing related health problems.
The importance of glucose fasting range cannot be overstated, as it provides valuable insights into glucose metabolism and can help identify potential health risks. By monitoring fasting glucose levels, individuals can assess their risk of developing insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. Moreover, understanding the glucose fasting range can help individuals make informed lifestyle choices, such as dietary changes, exercise routines, and stress management techniques, to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. In the following sections, we will explore the benefits of glucose fasting range, its working mechanisms, and provide practical examples and statistical data to illustrate its importance.
Benefits of Glucose Fasting Range
Working Mechanisms of Glucose Fasting Range
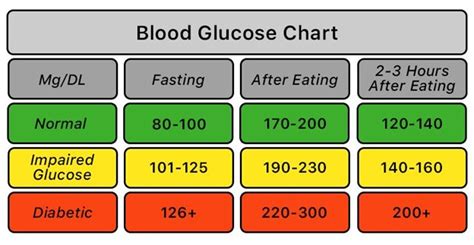
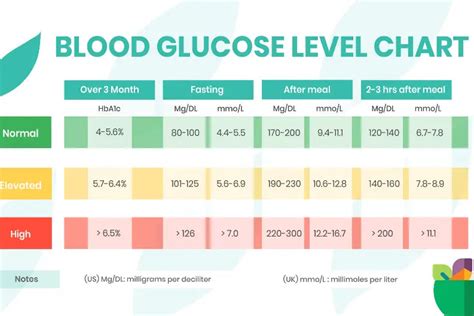
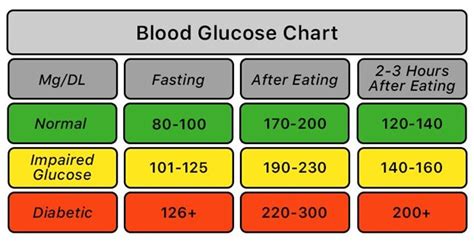
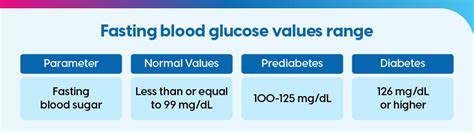
The working mechanisms of glucose fasting range involve the measurement of blood glucose levels after an overnight fast. This measurement is typically taken in the morning, before eating or drinking anything, and is used to assess glucose metabolism. The glucose fasting range is calculated based on the amount of glucose in the blood, which is measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The normal glucose fasting range is between 70-99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L), although this range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used.Normal Glucose Fasting Range
Abnormal Glucose Fasting Range
An abnormal glucose fasting range can be a sign of underlying health issues, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, or other metabolic disorders. The following are the different categories of abnormal glucose fasting range: * Impaired fasting glucose (IFG): 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) * Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher (7.0 mmol/L or higher) * Hypoglycemia: below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L)Factors That Influence Glucose Fasting Range
Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Studies have shown that maintaining a healthy glucose fasting range can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders. For example, a study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that individuals with a glucose fasting range of 70-99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L) had a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those with a glucose fasting range of 100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L). Additionally, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that lifestyle interventions, such as diet and exercise, can improve insulin sensitivity and lower glucose fasting range in individuals with insulin resistance.Steps to Maintain a Healthy Glucose Fasting Range
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, glucose fasting range is an essential indicator of glucose metabolism, and maintaining a healthy range can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders. By understanding the benefits, working mechanisms, and factors that influence glucose fasting range, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their blood sugar levels and improve overall health. Future studies should focus on developing personalized approaches to maintaining a healthy glucose fasting range, taking into account individual factors, such as age, sex, and lifestyle.What is the normal glucose fasting range?
+The normal glucose fasting range is between 70-99 mg/dL (3.9-5.5 mmol/L), although this range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used.
What factors can influence glucose fasting range?
+Several factors can influence glucose fasting range, including dietary factors, physical activity, sleep, stress, and medications.
How can I maintain a healthy glucose fasting range?
+Maintaining a healthy glucose fasting range requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions, including eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and monitoring blood sugar levels.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of glucose fasting range and its importance in maintaining overall health. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information.
