Intro
Discover 5 ways a higher sedimentation rate affects health, including inflammation, infection, and disease risks, with implications for erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) tests and medical diagnosis, revealing the importance of monitoring sedimentation rates for overall well-being.
The sedimentation rate, also known as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. A higher sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or other conditions. In this article, we will explore five ways a higher sedimentation rate can affect the body and what it may signify.
A higher sedimentation rate is often associated with various health conditions, including autoimmune disorders, infections, and cancers. The test is not diagnostic but rather a marker of inflammation. It is essential to understand the implications of a higher sedimentation rate and how it can impact overall health. By delving into the specifics of what a higher sedimentation rate may indicate, individuals can better comprehend their health status and the necessary steps to manage or alleviate underlying conditions.
The importance of understanding sedimentation rates lies in their ability to provide insight into the body's inflammatory response. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, but chronic or excessive inflammation can lead to various health issues. By monitoring sedimentation rates, healthcare providers can assess the level of inflammation and make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of conditions. This understanding can lead to more effective healthcare strategies and improved patient outcomes.
Introduction to Sedimentation Rate
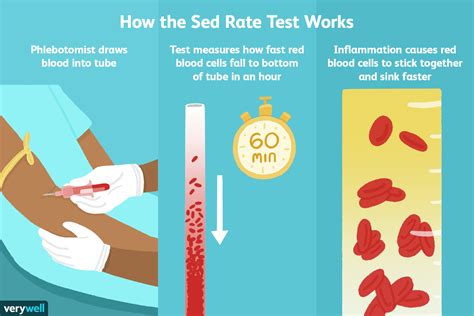
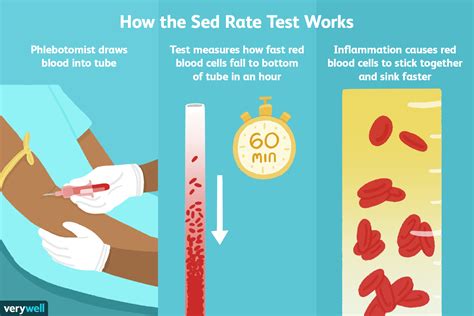
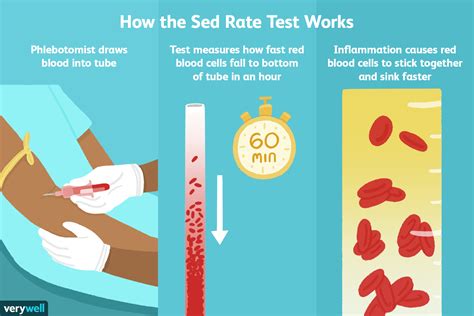
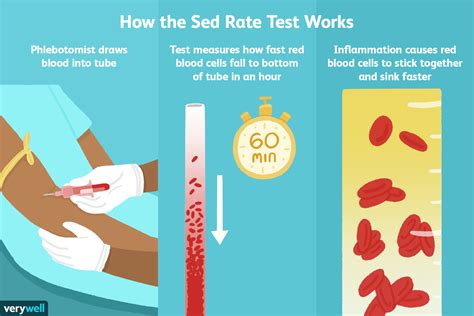
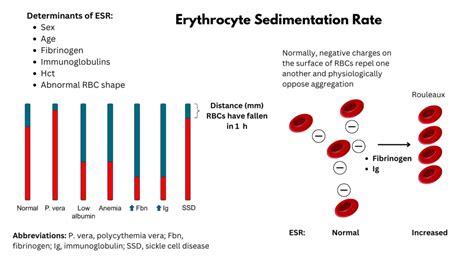
The sedimentation rate is a simple yet informative test that has been used for decades to assess inflammation levels. It works by measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle in a test tube. Normally, red blood cells settle slowly, but in the presence of inflammation, they clump together and settle more quickly. This increased settling rate is what the test measures, providing a gauge of the body's inflammatory state.
How Sedimentation Rate Works
The process of conducting a sedimentation rate test is straightforward. A blood sample is taken from the patient, and then an anticoagulant is added to prevent the blood from clotting. The blood sample is placed in a tall, narrow tube, and the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube is measured over a specified period, usually one hour. The result is reported in millimeters per hour (mm/h). The reference range for sedimentation rate can vary slightly between laboratories but generally falls within specific limits for adults.Conditions Associated with Higher Sedimentation Rate
A higher sedimentation rate can be associated with a variety of conditions, including but not limited to infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer. Infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and pelvic inflammatory disease can cause an increase in sedimentation rate. Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis also often result in elevated sedimentation rates due to the body's immune response.
Autoimmune Diseases and Sedimentation Rate
Autoimmune diseases are conditions where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. These diseases can lead to chronic inflammation, which in turn can cause a higher sedimentation rate. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, the immune system attacks the lining of the joints, leading to inflammation and potentially an elevated sedimentation rate. Similarly, in lupus, the immune system can attack various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, and organs, resulting in inflammation and a higher sedimentation rate.Impact of Higher Sedimentation Rate on Health
A higher sedimentation rate can have significant implications for health, indicating the presence of underlying conditions that require medical attention. Chronic inflammation, as suggested by a persistently elevated sedimentation rate, can lead to the development of more severe health issues, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Therefore, it is crucial to identify and manage the underlying causes of inflammation to prevent long-term health consequences.
Management and Treatment
The management and treatment of conditions associated with a higher sedimentation rate depend on the underlying cause. For infections, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. For autoimmune diseases, treatments such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics may be used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. In some cases, lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and stress management, can also help in reducing inflammation and improving overall health.Monitoring Sedimentation Rate Over Time
Monitoring sedimentation rate over time can provide valuable information about the progression of a condition and the effectiveness of treatment. A decrease in sedimentation rate can indicate that treatment is working and inflammation is being managed, while an increase can suggest that the condition is worsening or that adjustments to treatment are needed. Regular monitoring can help healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care and can assist in the early detection of potential complications.
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups are essential for maintaining good health and detecting potential issues early. These check-ups can include a variety of tests, such as sedimentation rate, to assess overall health and identify any areas of concern. By staying on top of health through regular check-ups and monitoring, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing and managing health conditions, leading to better outcomes and improved quality of life.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, a higher sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation or underlying health conditions. Understanding the implications of a higher sedimentation rate and taking appropriate action can lead to better health outcomes. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can manage conditions associated with a higher sedimentation rate and reduce the risk of long-term health consequences. It is essential to approach health proactively, staying informed and engaged in the management of one's health.
Final Thoughts
The sedimentation rate is a valuable tool in the assessment of inflammation and overall health. By recognizing the significance of a higher sedimentation rate and the conditions it may indicate, individuals can take the first steps towards addressing underlying health issues. Through a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, it is possible to manage conditions associated with a higher sedimentation rate and improve overall well-being.What does a higher sedimentation rate indicate?
+A higher sedimentation rate can indicate the presence of inflammation, infection, or other conditions in the body. It is not diagnostic but rather a marker of inflammation.
How is sedimentation rate measured?
+Sedimentation rate is measured by taking a blood sample, adding an anticoagulant, and then measuring the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube over a specified period.
What conditions are associated with a higher sedimentation rate?
+A variety of conditions, including infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer, can be associated with a higher sedimentation rate. Examples include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences regarding sedimentation rate and its implications for health. Your comments and questions can help others better understand this important health indicator. Additionally, consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information, and do not hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.
