Intro
Discover 5 uses of Hydralazine, a vasodilator medication, for hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions, exploring its benefits and applications in blood pressure management and cardiovascular health.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a widespread health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. It can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage, if left unmanaged. One of the medications used to treat high blood pressure is hydralazine. Hydralazine is a vasodilator, which means it works by relaxing the muscles in the blood vessel walls, causing them to dilate. This dilation reduces blood pressure, making it easier for the heart to pump blood.
The importance of managing hypertension cannot be overstated. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to a range of serious health problems, including heart failure, coronary artery disease, and renal failure. Given the potential consequences of untreated hypertension, it is crucial to understand the role of medications like hydralazine in blood pressure management. Hydralazine is often prescribed in combination with other medications to achieve optimal blood pressure control. Its effectiveness, potential side effects, and the conditions it treats make it a valuable option for healthcare providers.
Understanding how hydralazine works and its various applications can help patients better manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Hydralazine's mechanism of action, its benefits, and its potential drawbacks are essential topics for discussion. Furthermore, exploring the different conditions that hydralazine can treat, beyond just hypertension, can provide insight into its versatility as a therapeutic agent. By delving into these aspects, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of hydralazine's role in modern medicine and how it contributes to the management of cardiovascular health.
Introduction to Hydralazine

Hydralazine is a direct vasodilator that is primarily used to treat high blood pressure. It is often used in combination with other antihypertensive drugs to achieve better control over blood pressure levels. The drug works by directly relaxing the smooth muscles in the wall of arterioles, which causes the vessels to dilate. This dilation reduces peripheral resistance, lowers blood pressure, and increases cardiac output. Hydralazine is also used in the management of heart failure, as it can help reduce the workload on the heart by decreasing the resistance the heart must pump against.
Benefits of Hydralazine
The benefits of hydralazine include its ability to effectively lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, and improve symptoms in patients with heart failure. It is particularly useful in patients who have not responded adequately to other antihypertensive therapies. Additionally, hydralazine can be used in pregnant women with severe hypertension, as it is considered relatively safe for use during pregnancy.Uses of Hydralazine

Hydralazine has several clinical applications beyond the treatment of essential hypertension. Some of the notable uses include:
- Hypertensive Crisis: Hydralazine can be used to manage hypertensive emergencies, especially in pregnant women with preeclampsia or eclampsia.
- Heart Failure: It is used in the treatment of heart failure, particularly in patients with reduced ejection fraction, as part of a combination therapy to reduce afterload and improve cardiac output.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Although not the first line of treatment, hydralazine can be considered in certain cases of pulmonary hypertension, especially when used in combination with other vasodilators.
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Hydralazine may be used off-label to treat Raynaud’s phenomenon, a condition that affects blood flow to the fingers and toes, and sometimes the ears, nose, and lips.
- Scleroderma: In some cases, hydralazine is prescribed for patients with scleroderma, an autoimmune disorder that can cause blood vessels to narrow and hardened skin, to help manage associated vascular symptoms.
Working Mechanism of Hydralazine
Hydralazine's primary mechanism of action involves the direct relaxation of smooth muscle in the walls of arterioles. This action leads to a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance, which in turn lowers arterial blood pressure. The reduction in blood pressure decreases the workload on the heart, improving cardiac output in conditions like heart failure. The exact biochemical mechanism behind hydralazine's vasodilatory effect is not fully understood but is thought to involve alterations in ion flux across cell membranes and the interference with calcium ion influx into vascular smooth muscle.Administration and Dosage

The administration and dosage of hydralazine can vary depending on the condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication. For the treatment of hypertension, hydralazine is typically started at a low dose and gradually increased until the desired blood pressure response is achieved. It is essential to monitor patients for potential side effects, such as reflex tachycardia, sodium retention, and lupus-like syndrome, especially with long-term use.
Potential Side Effects
While hydralazine is effective in managing hypertension and other conditions, it can cause several side effects. Common side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. More severe side effects, such as a lupus-like syndrome, can occur with prolonged use. It is crucial for patients to report any unusual symptoms to their healthcare provider to ensure timely management of potential side effects.Interactions and Contraindications
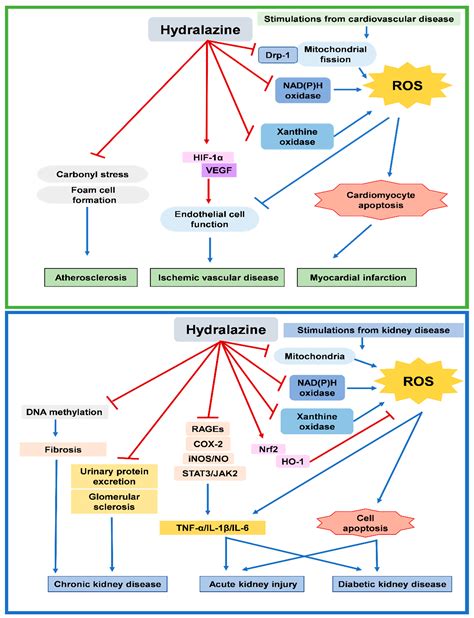
Hydralazine can interact with several medications, including beta-blockers, which can enhance its hypotensive effect, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can reduce its effectiveness. It is also contraindicated in patients with coronary artery disease, as it can cause reflex tachycardia, which may increase myocardial oxygen demand. Patients with a history of lupus should avoid hydralazine due to the risk of exacerbating the condition.
Precautions and Warnings
Patients taking hydralazine should be aware of several precautions and warnings. It is essential to monitor blood pressure regularly to avoid hypotension. Patients should also be cautious when changing positions to avoid orthostatic hypotension. Hydralazine can cause sodium retention, leading to edema, so patients should be monitored for signs of fluid overload.Conclusion and Future Directions
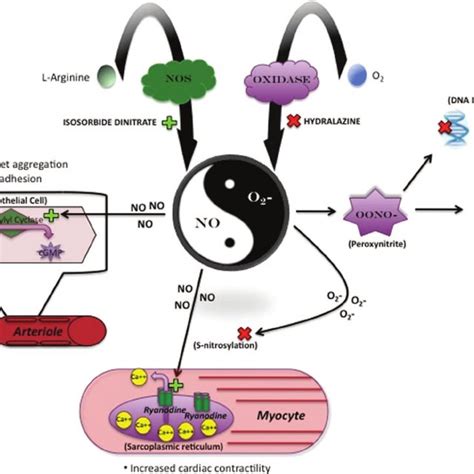
In conclusion, hydralazine is a valuable medication in the management of hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions. Its effectiveness, combined with its relatively safe profile, especially in pregnancy, makes it a crucial component of antihypertensive therapy. As research continues to unravel the complexities of cardiovascular diseases, the role of hydralazine and similar vasodilators may evolve, offering new avenues for the treatment of these conditions. It is essential for healthcare providers and patients to stay informed about the latest developments and guidelines regarding the use of hydralazine to ensure its safe and effective use.
Final Thoughts
The management of hypertension and related conditions requires a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle modifications, monitoring, and, when necessary, medication. Hydralazine, with its direct vasodilatory effects, plays a significant role in this management. By understanding its uses, benefits, and potential side effects, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve better control over their blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about hydralazine and its uses in the comments section below. Your input can help others better understand this medication and its role in managing hypertension and other health conditions.
What is hydralazine used for?
+Hydralazine is primarily used to treat high blood pressure. It is also used in the management of heart failure and can be used in hypertensive emergencies, especially in pregnant women.
How does hydralazine work?
+Hydralazine works by directly relaxing the smooth muscles in the walls of arterioles, causing them to dilate. This dilation reduces peripheral resistance and lowers blood pressure.
What are the potential side effects of hydralazine?
+Common side effects of hydralazine include headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. More severe side effects can include a lupus-like syndrome, especially with long-term use.
