Intro
Discover the effects of 5mg Diazepam, a mild benzodiazepine dose, and explore its strength, uses, and potential side effects, including anxiety relief and muscle relaxation, to understand its impact on mental health and wellness.
Diazepam, commonly known by its brand name Valium, is a benzodiazepine that has been widely used for its therapeutic effects, which include relieving anxiety, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, muscle spasms, and as a sedative before surgeries or medical procedures. The medication works by enhancing the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, which is a neurotransmitter that inhibits brain activity, leading to a calming effect. The question of whether 5mg of Diazepam is strong depends on various factors, including the individual's health, age, and their sensitivity to the drug.
The dosage of Diazepam can vary widely, from 2mg to 10mg for anxiety disorders and even higher for severe conditions or in certain medical procedures. A dose of 5mg is considered moderate and is often prescribed for the management of anxiety disorders, symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal, and for muscle spasms. For many patients, 5mg of Diazepam can provide significant relief from their symptoms without causing excessive sedation or other side effects. However, the perception of its strength can vary significantly from person to person.
Understanding Diazepam Dosage

The dosage of Diazepam is tailored to the individual's response to the medication. While 5mg may be sufficient for some, others might require higher doses to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Factors such as age, weight, and liver function can influence how the body metabolizes Diazepam, thereby affecting its efficacy and side effect profile. For the elderly or those with compromised liver function, even a dose of 5mg might be considered strong due to the potential for increased sedation and risk of falls or other adverse effects.
Benefits and Risks of 5mg Diazepam
The benefits of using 5mg of Diazepam include its rapid onset of action, providing quick relief from anxiety and other conditions it is prescribed for. However, like all medications, Diazepam comes with potential risks and side effects, especially at higher doses. Common side effects include drowsiness, fatigue, muscle weakness, and ataxia (lack of coordination). Less common but more serious side effects can include anterograde amnesia (difficulty forming new memories), paradoxical reactions (such as increased anxiety or agitation), and dependence.How Diazepam Works
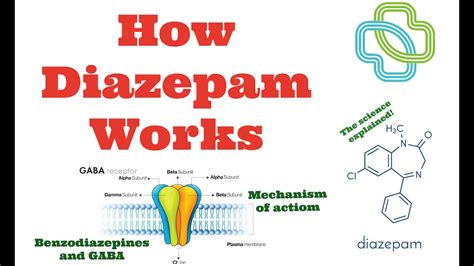
Diazepam works by enhancing the effect of the neurotransmitter GABA, which is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. By facilitating the action of GABA, Diazepam increases the inhibitory effects on the nervous system, leading to a calming effect on the brain and nervous system. This mechanism of action underlies its therapeutic effects in treating anxiety, insomnia, and seizures, among other conditions.
Steps for Safe Use
To use Diazepam safely, especially at a dose of 5mg, several steps should be followed: - **Consult a Doctor:** Always start Diazepam under the guidance of a healthcare provider. They can assess whether Diazepam is appropriate for your condition and determine the right dose. - **Follow Instructions:** Adhere strictly to the prescribed dosage and schedule. Do not increase the dose without consulting your doctor. - **Monitor Side Effects:** Be aware of potential side effects and report them to your doctor. This is especially important if you experience severe or unusual side effects. - **Avoid Alcohol and Other CNS Depressants:** Combining Diazepam with alcohol or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants can enhance sedative effects and increase the risk of respiratory depression, a potentially life-threatening condition.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Studies have shown that Diazepam is effective in managing anxiety disorders and other conditions. For instance, in clinical trials, Diazepam has been shown to significantly reduce symptoms of anxiety in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Statistical data also indicate that the use of benzodiazepines like Diazepam is common among individuals with anxiety disorders, highlighting the need for careful prescribing practices to minimize the risk of dependence and other adverse effects.
Key Information Related to Diazepam Use
Key points to consider when using Diazepam include: - **Dependence and Withdrawal:** Diazepam can lead to physical dependence. Stopping the medication abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms, which can be severe. Gradual tapering under medical supervision is recommended when discontinuing Diazepam. - **Interactions with Other Medications:** Diazepam can interact with other medications, including antidepressants, antihistamines, and other CNS depressants, increasing the risk of adverse effects. - **Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:** Diazepam should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as it can pass through the placenta and into breast milk, potentially affecting the fetus or baby.Benefits of Diazepam

The benefits of Diazepam are numerous and include rapid relief from anxiety and insomnia, effectiveness in managing acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and muscle relaxant properties. Diazepam's fast onset of action makes it particularly useful in emergency situations, such as status epilepticus (a medical emergency characterized by prolonged or recurrent seizures).
Working Mechanisms and Steps for Administration
The working mechanism of Diazepam, as mentioned, involves the enhancement of GABA activity in the brain. For administration, Diazepam is available in various forms, including oral tablets, liquid solutions, and rectal tubes for severe seizures. The steps for administration depend on the form of the medication and the condition being treated. Generally, oral Diazepam is taken 2-4 times a day, as directed by a healthcare provider.Practical Examples and Case Studies

Case studies and practical examples illustrate the efficacy and safety of Diazepam in various clinical settings. For instance, a patient with a history of generalized anxiety disorder may find significant relief with a dose of 5mg of Diazepam, taken twice daily, allowing them to manage their symptoms effectively and improve their quality of life.
Steps to Minimize Risks
To minimize the risks associated with Diazepam use, several steps can be taken: - **Regular Monitoring:** Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider to monitor the effectiveness of the medication and potential side effects. - **Dose Adjustment:** Adjusting the dose based on the patient's response and side effect profile. - **Education:** Educating patients about the potential risks, including dependence, and the importance of not sharing their medication with others.SEO Optimization and Readability

To ensure that information about Diazepam and its uses is accessible and understandable, content should be optimized for readability and search engine optimization (SEO). This involves using clear and concise language, organizing content into logical sections, and incorporating relevant keywords without keyword stuffing.
Encouraging Engagement
Readers are encouraged to share their experiences or ask questions about Diazepam in the comments section below. Sharing personal stories or seeking advice from others can provide valuable insights and support. Additionally, readers can share this article with others who might benefit from the information, helping to spread awareness about the safe and effective use of Diazepam.What is Diazepam used for?
+Diazepam is used for its therapeutic effects in relieving anxiety, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, muscle spasms, and as a sedative before surgeries or medical procedures.
Is 5mg of Diazepam strong?
+The perception of the strength of 5mg of Diazepam can vary significantly from person to person, depending on factors such as age, health, and sensitivity to the drug.
How does Diazepam work?
+Diazepam works by enhancing the effect of the neurotransmitter GABA in the brain, leading to a calming effect on the nervous system.
