The opioid crisis has been a major concern for healthcare professionals and the general public alike, with its impact being felt across the globe. Opioids are a class of drugs that are commonly used to treat pain, but they can also be highly addictive and have serious side effects. Despite their potential risks, opioids remain a widely used medication, and it's essential to understand the facts about them. In this article, we will delve into the world of opioids, exploring their history, benefits, risks, and the current state of the opioid crisis.
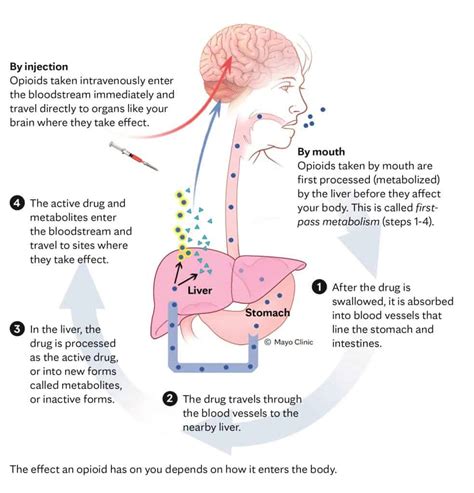
Opioids have been used for centuries to treat pain, with the earliest recorded use dating back to ancient civilizations. The word "opium" is derived from the Greek word for juice, which refers to the sap of the opium poppy plant. Opioids work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, which can help to reduce pain perception. However, they can also produce feelings of euphoria, which can lead to addiction. The opioid crisis has highlighted the need for a balanced approach to pain management, one that takes into account the potential benefits and risks of opioids.
The opioid crisis has had a devastating impact on communities around the world, with millions of people affected by opioid addiction. The crisis has been driven by a combination of factors, including overprescription, lack of education, and the rise of illicit opioid use. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need for alternative approaches to pain management, including non-pharmacological interventions and medication-assisted treatment. By understanding the facts about opioids, we can work towards a more informed and compassionate approach to addressing the opioid crisis.
What Are Opioids?
Opioids are a class of drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant or synthesized in a laboratory. They work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, which can help to reduce pain perception. Opioids can be used to treat a range of conditions, including chronic pain, acute pain, and coughs. However, they can also produce serious side effects, including addiction, respiratory depression, and constipation. There are several types of opioids, including natural opioids, semi-synthetic opioids, and synthetic opioids. Natural opioids, such as morphine and codeine, are derived from the opium poppy plant, while semi-synthetic opioids, such as oxycodone and hydrocodone, are created in a laboratory using natural opioids as a starting point. Synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl and methadone, are entirely man-made and can be much more potent than natural or semi-synthetic opioids.
Benefits of Opioids
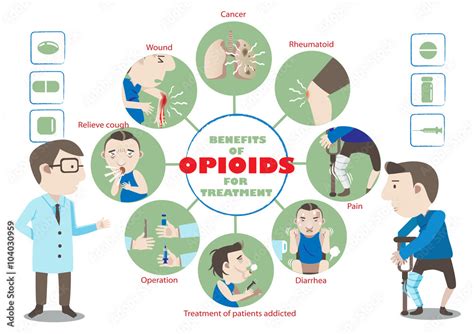
Opioids can be an effective treatment for pain, particularly for acute pain and chronic pain that is severe and debilitating. They can help to reduce pain perception, improve mood, and enhance quality of life. Opioids can also be used to treat other conditions, such as coughs and diarrhea. However, the benefits of opioids must be carefully weighed against the potential risks, including addiction, overdose, and side effects. When used responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, opioids can be a valuable tool for managing pain and improving quality of life. Some of the benefits of opioids include:
* Effective pain relief
* Improved mood
* Enhanced quality of life
* Treatment of other conditions, such as coughs and diarrhea
* Can be used in combination with other medications for enhanced pain relief
Risks of Opioids
Despite their potential benefits, opioids carry significant risks, including addiction, overdose, and side effects. Opioid addiction can occur when an individual takes opioids regularly, leading to physical dependence and tolerance. Overdose can occur when an individual takes too much of an opioid, leading to respiratory depression and even death. Side effects of opioids can include constipation, nausea, and drowsiness. The risks of opioids must be carefully considered when prescribing or taking these medications. Some of the risks of opioids include:
* Addiction
* Overdose
* Side effects, such as constipation and nausea
* Respiratory depression
* Increased risk of falls and accidents
* Interactions with other medications
Opioid Crisis
The opioid crisis has had a devastating impact on communities around the world, with millions of people affected by opioid addiction. The crisis has been driven by a combination of factors, including overprescription, lack of education, and the rise of illicit opioid use. In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need for alternative approaches to pain management, including non-pharmacological interventions and medication-assisted treatment. The opioid crisis has highlighted the need for a balanced approach to pain management, one that takes into account the potential benefits and risks of opioids. Some of the key statistics related to the opioid crisis include:
* Millions of people affected by opioid addiction
* Thousands of deaths due to opioid overdose
* Billions of dollars spent on opioid-related healthcare costs
* Increased risk of opioid addiction among certain populations, such as those with a history of substance abuse
Alternative Approaches to Pain Management
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the need for alternative approaches to pain management, including non-pharmacological interventions and medication-assisted treatment. Non-pharmacological interventions can include techniques such as acupuncture, massage, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. Medication-assisted treatment can include the use of medications such as buprenorphine and methadone to treat opioid addiction. Alternative approaches to pain management can help to reduce the risk of opioid addiction and overdose, while also providing effective pain relief. Some of the alternative approaches to pain management include:
* Non-pharmacological interventions, such as acupuncture and massage
* Medication-assisted treatment, such as buprenorphine and methadone
* Alternative medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antidepressants
* Lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and stress reduction
Prevention and Education
Prevention and education are critical components of addressing the opioid crisis. By educating individuals about the risks and benefits of opioids, we can help to reduce the risk of opioid addiction and overdose. Prevention strategies can include initiatives such as prescription monitoring programs, safe disposal of unused medications, and community-based education programs. Education can include information about the risks and benefits of opioids, as well as alternative approaches to pain management. Some of the prevention and education strategies include:
* Prescription monitoring programs
* Safe disposal of unused medications
* Community-based education programs
* Public awareness campaigns
* Healthcare provider education and training
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment and recovery from opioid addiction are complex and multifaceted processes. Treatment can include medication-assisted treatment, behavioral therapy, and support groups. Recovery can involve a range of activities, including counseling, support groups, and lifestyle modifications. The goal of treatment and recovery is to help individuals achieve long-term sobriety and improve their overall quality of life. Some of the treatment and recovery options include:
* Medication-assisted treatment, such as buprenorphine and methadone
* Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy
* Support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous
* Counseling, such as individual and group counseling
* Lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and stress reduction
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment is a type of treatment that uses medications such as buprenorphine and methadone to treat opioid addiction. These medications can help to reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings, making it easier for individuals to achieve sobriety. Medication-assisted treatment can be used in combination with behavioral therapy and support groups for enhanced effectiveness.
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy is a type of treatment that focuses on changing behaviors and thought patterns associated with opioid addiction. Cognitive-behavioral therapy is a type of behavioral therapy that can help individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors. Behavioral therapy can be used in combination with medication-assisted treatment and support groups for enhanced effectiveness.
What are the most common types of opioids?
+
The most common types of opioids include natural opioids, semi-synthetic opioids, and synthetic opioids. Natural opioids, such as morphine and codeine, are derived from the opium poppy plant, while semi-synthetic opioids, such as oxycodone and hydrocodone, are created in a laboratory using natural opioids as a starting point. Synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl and methadone, are entirely man-made and can be much more potent than natural or semi-synthetic opioids.
What are the risks of opioid addiction?
+
The risks of opioid addiction include overdose, respiratory depression, and increased risk of falls and accidents. Opioid addiction can also lead to social and economic problems, such as loss of employment and relationships. Additionally, opioid addiction can increase the risk of infectious diseases, such as HIV and hepatitis, through shared needle use.
How can I prevent opioid addiction?
+
To prevent opioid addiction, it's essential to use opioids only as directed by a healthcare provider and to follow safe storage and disposal practices. Additionally, individuals can reduce their risk of opioid addiction by avoiding illicit opioid use, seeking alternative approaches to pain management, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of opioid addiction.
As we conclude our exploration of the world of opioids, it's essential to remember that opioid addiction is a complex and multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive and compassionate approach. By understanding the facts about opioids, we can work towards a more informed and balanced approach to pain management, one that takes into account the potential benefits and risks of opioids. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with opioids, and to join the conversation about how we can work together to address the opioid crisis. Whether you're a healthcare provider, a patient, or simply a concerned citizen, your voice matters, and your contributions can help to make a difference in the lives of those affected by opioid addiction. So, let's keep the conversation going, and work together to create a brighter, healthier future for all.