Intro
Discover how beta blockers work to reduce blood pressure, alleviate anxiety, and regulate heart rate, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and uses in managing hypertension, angina, and heart failure.
The use of beta blockers has become increasingly prevalent in the medical field, particularly in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. These medications have been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular-related deaths. But how exactly do beta blockers work? Understanding the mechanisms behind these medications can provide valuable insights into their benefits and potential side effects. In this article, we will delve into the world of beta blockers, exploring their working mechanisms, benefits, and potential applications.
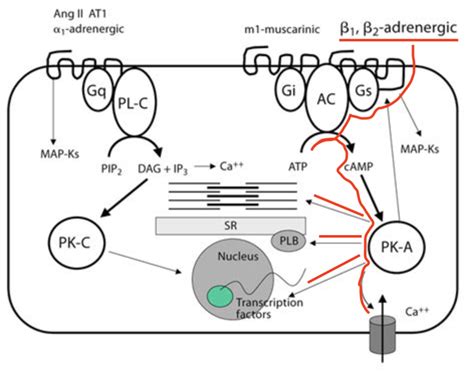
Beta blockers are a class of medications that work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, on the body. Epinephrine is a stress hormone that is released in response to physical or emotional stress, causing the heart to beat faster and stronger. By blocking the effects of epinephrine, beta blockers reduce the heart rate and blood pressure, which can help to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular conditions. But beta blockers do more than just reduce heart rate and blood pressure; they also have a range of other effects on the body.
The importance of understanding how beta blockers work cannot be overstated. With the rising prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the medications used to treat these conditions. By exploring the mechanisms behind beta blockers, we can gain a better understanding of their potential benefits and side effects, as well as their potential applications in the treatment of various medical conditions. In this article, we will provide an in-depth examination of the working mechanisms of beta blockers, including their effects on the heart, blood vessels, and other bodily systems.
How Beta Blockers Reduce Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Blocking Beta Receptors
Beta blockers work by blocking the beta receptors in the heart and blood vessels. Beta receptors are specialized proteins that are embedded in the cell membranes of the heart and blood vessels. When epinephrine binds to these receptors, it causes the heart to beat faster and stronger, and the blood vessels to constrict. By blocking these receptors, beta blockers prevent epinephrine from binding, which reduces the heart rate and blood pressure. This can help to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular conditions.The Benefits of Beta Blockers
Reducing the Risk of Heart Attacks and Strokes
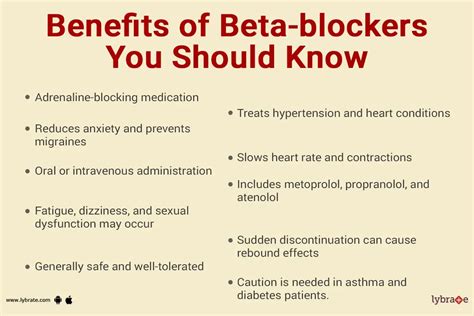
One of the most significant benefits of beta blockers is their ability to reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes. By reducing the heart rate and blood pressure, beta blockers can help to alleviate the strain on the heart and blood vessels, which can reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, beta blockers can help to prevent the formation of blood clots, which can reduce the risk of strokes and other cardiovascular-related deaths.The Different Types of Beta Blockers
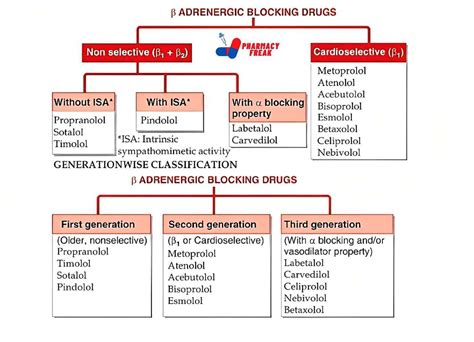
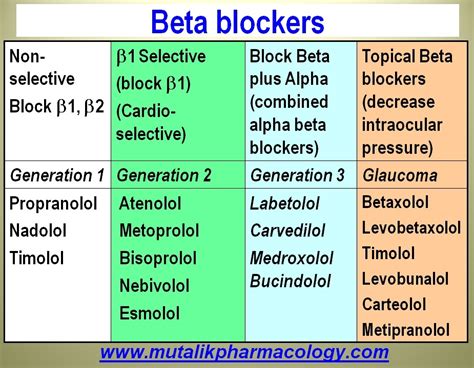
Non-Selective Beta Blockers
Non-selective beta blockers are a type of beta blocker that blocks both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. These medications are often used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure, angina, and heart failure. Non-selective beta blockers can be effective in reducing the heart rate and blood pressure, but they can also have a range of side effects, including fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath.Potential Side Effects of Beta Blockers
Managing Side Effects
Managing side effects is an essential part of taking beta blockers. If you experience any side effects while taking beta blockers, it is essential to speak with your doctor. Your doctor may be able to adjust your dosage or switch you to a different medication. Additionally, there are several things you can do to manage side effects, such as taking your medication with food, staying hydrated, and getting regular exercise.Conclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
As we move forward, it is essential to continue researching the effects of beta blockers on the body. By understanding how beta blockers work, we can gain a better understanding of their potential benefits and side effects, as well as their potential applications in the treatment of various medical conditions. Whether you are a healthcare professional or simply someone who is interested in learning more about beta blockers, we hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of these medications and their effects on the body.What are beta blockers and how do they work?
+Beta blockers are a class of medications that work by blocking the effects of epinephrine on the heart and blood vessels. They reduce the heart rate and blood pressure, which can help to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular conditions.
What are the benefits of taking beta blockers?
+The benefits of taking beta blockers include reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular-related deaths. They can also help to improve survival rates in patients with heart failure and reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death.
What are the potential side effects of beta blockers?
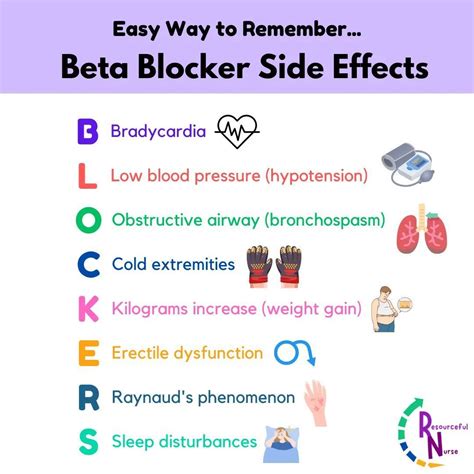
+Potential side effects of beta blockers include fatigue, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Other potential side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In rare cases, beta blockers can also cause more serious side effects, such as heart failure, bronchospasm, and allergic reactions.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of beta blockers and their effects on the body. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to reach out. We would love to hear from you and help you learn more about this important topic. Whether you are a healthcare professional or simply someone who is interested in learning more about beta blockers, we encourage you to share this article with others and continue the conversation. Together, we can work to improve our understanding of beta blockers and their potential applications in the treatment of various medical conditions.
