Intro
Discover what Alanine Transaminase means, its role in liver health, and how ALT levels impact diagnosis, treatment, and enzyme function in medical tests.
The importance of liver health cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in detoxifying the body, regulating metabolism, and maintaining overall well-being. One key indicator of liver health is the level of certain enzymes in the blood, including Alanine Transaminase (ALT). ALT is an enzyme that is primarily found in the liver, and elevated levels of ALT in the blood can indicate liver damage or disease. In this article, we will delve into the world of ALT, exploring what it means, how it is measured, and what the results can indicate about liver health.
Understanding the role of ALT in the body is essential for appreciating its significance in liver health. ALT is one of several enzymes that are involved in the breakdown and synthesis of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. When the liver is damaged, ALT is released into the bloodstream, where it can be measured using a blood test. The level of ALT in the blood is a key indicator of liver health, and elevated levels can indicate a range of conditions, from mild liver damage to severe liver disease.
The measurement of ALT levels is a routine part of medical check-ups, particularly for individuals who are at risk of liver disease. The test is typically performed using a blood sample, which is then analyzed in a laboratory to determine the level of ALT in the blood. The results are usually reported in units per liter (U/L), and the normal range for ALT levels can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. In general, however, ALT levels are considered to be within the normal range if they are below 40 U/L.
What is Alanine Transaminase?
How is Alanine Transaminase Measured?
The measurement of ALT levels is a routine part of medical check-ups, particularly for individuals who are at risk of liver disease. The test is typically performed using a blood sample, which is then analyzed in a laboratory to determine the level of ALT in the blood. The results are usually reported in units per liter (U/L), and the normal range for ALT levels can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors.What Do Alanine Transaminase Results Mean?
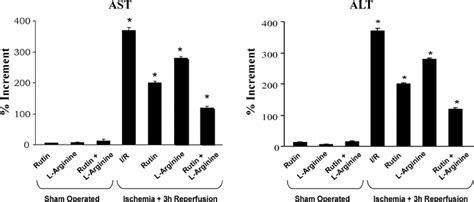
- Normal ALT levels: These are typically below 40 U/L, although the normal range can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors.
- Mildly elevated ALT levels: These are typically between 40 U/L and 120 U/L, and can indicate mild liver damage or inflammation.
- Moderately elevated ALT levels: These are typically between 120 U/L and 240 U/L, and can indicate moderate liver damage or inflammation.
- Severely elevated ALT levels: These are typically above 240 U/L, and can indicate severe liver damage or disease.
What Can Cause Elevated Alanine Transaminase Levels?
There are several possible causes of elevated ALT levels, including:- Liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis
- Liver damage, such as that caused by a viral infection or exposure to toxins
- Fatty liver disease, which is a condition in which excess fat builds up in the liver
- Pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas
- Muscle damage, such as that caused by a muscle injury or muscle disease
- Certain medications, such as statins or antibiotics
How is Alanine Transaminase Used in Medical Diagnosis?

- Diagnosing liver disease, such as hepatitis or cirrhosis
- Monitoring liver disease, such as tracking the progression of liver damage or the response to treatment
- Evaluating liver function, such as assessing the liver's ability to detoxify the body and regulate metabolism
- Screening for liver disease, such as identifying individuals who are at risk of liver disease due to factors such as obesity or family history
What Are the Benefits of Monitoring Alanine Transaminase Levels?
Monitoring ALT levels can provide several benefits, including:- Early detection of liver disease, which can improve treatment outcomes and reduce the risk of complications
- Tracking the progression of liver disease, which can help guide treatment decisions and monitor the effectiveness of therapy
- Evaluating liver function, which can help identify individuals who are at risk of liver disease or who may benefit from lifestyle modifications or medical interventions
- Reducing the risk of liver damage, which can be caused by factors such as excessive alcohol consumption or exposure to toxins
How Can Alanine Transaminase Levels Be Reduced?
- Losing weight, which can reduce the risk of fatty liver disease and improve liver function
- Exercising regularly, which can improve liver function and reduce the risk of liver disease
- Eating a healthy diet, which can provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support liver health
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, which can damage the liver and increase the risk of liver disease
- Avoiding exposure to toxins, which can damage the liver and increase the risk of liver disease
- Taking medications as directed, which can help manage liver disease and reduce the risk of complications
What Are the Risks of Elevated Alanine Transaminase Levels?
Elevated ALT levels can indicate liver damage or disease, which can increase the risk of complications such as:- Liver failure, which can be life-threatening and require a liver transplant
- Liver cancer, which can be caused by chronic liver damage or inflammation
- Cirrhosis, which can cause scarring of the liver and increase the risk of liver failure
- Fatty liver disease, which can increase the risk of liver damage and liver disease
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about ALT and liver health in the comments section below. If you have any concerns about your liver health or would like to learn more about ALT, please consult with a healthcare professional. You can also share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about ALT and liver health.
What is the normal range for Alanine Transaminase levels?
+The normal range for ALT levels can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. However, in general, ALT levels are considered to be within the normal range if they are below 40 U/L.
What can cause elevated Alanine Transaminase levels?
+Elevated ALT levels can be caused by a range of factors, including liver disease, liver damage, fatty liver disease, pancreatitis, muscle damage, and certain medications.
How can Alanine Transaminase levels be reduced?
+Reducing ALT levels can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, including losing weight, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and avoiding exposure to toxins.
